Fig. 6.
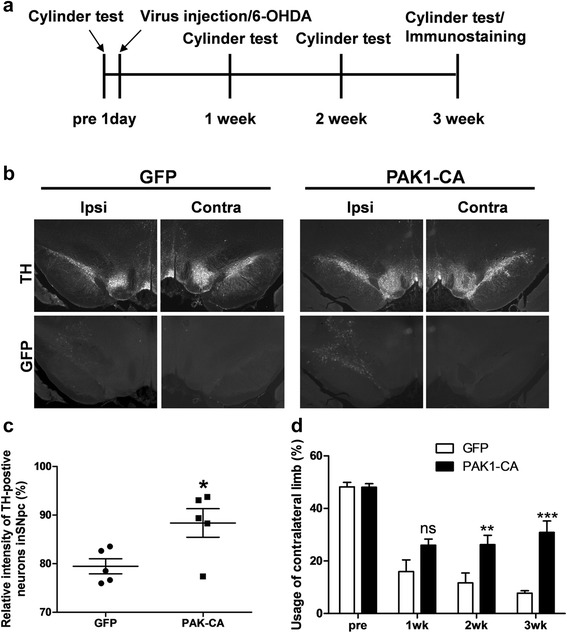
PAK1-CA expression recovers behavioral defect and loss of mesencephalic dopamine neurons. a Experimental scheme and procedure. b Lentiviruses encoding GFP or PAK1-CA were infused into the right SNpc at rate of 0.5 μl/min at the following coordinates: anteroposterior, −5.3 mm from the bregma; mediolateral, 2.3 mm; dorsoventral, −7.3 mm below surface of the dura. After 3 weeks, the midbrain tissue sections were immunostained with anti-Tyrosine Hyroxylase antibody and visualized by immunostaining using Cy3-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody. c The loss of DA neurons in the SNpc induced by 6-OHDA treatment was blocked by PAK1-CA expression, but not by GFP expression (GFP: 79.5 ± 1.55 %, n = 5, compared to the ipsilateral side; PAK1-CA: 88.4 ± 2.94 %, n = 5, compare to ipsilateral side, Student’s t-tests, *P < 0.05). d PAK1-CA expression significantly improved usage of the contralateral limb in a hemiparkinsonian animal model (GFP: PAK1-CA, pretest, 48.2 ± 1.69, n = 5: 48.08 ± 1.37, n = 8; 1 week, 16.0 ± 4.46, n = 5: 26.00 ± 2.30, n = 8; 2 weeks, 11.7 ± 3.73, n = 5: 26.21 ± 3.58, n = 8; 3 weeks, 7.8 ± 0.93, n = 4: 30.88 ± 4.32, n = 6; Two-way ANOVA, F 3,41 = 39.40, ***P < 0.0001, Bonferroni multiple comparison tests, ns: not significant, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
