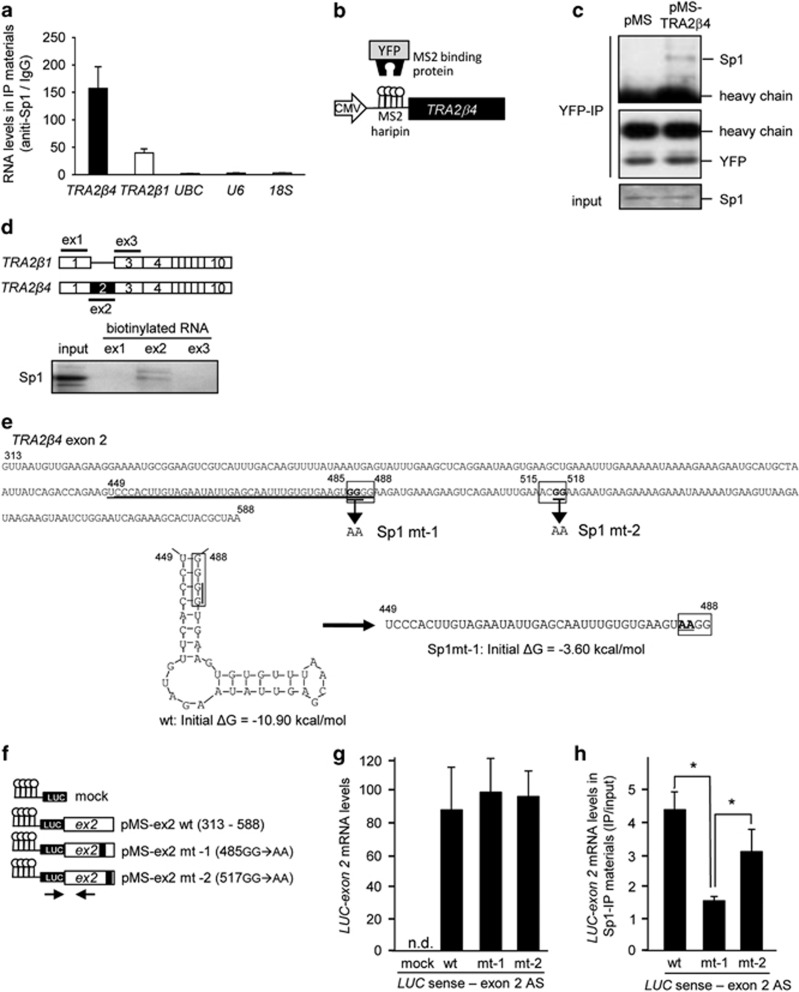
Figure 6.
TRA2β4 binds to Sp1 via exon 2. (a) Nuclear lysates prepared from UV-crosslinked HCT116 cells were subjected to an RIP assay using an anti-Sp1 antibody or normal mouse IgG. Immunoprecipitated RNAs were quantified by qPCR. Data are shown as enrichment relative to values obtained with normal mouse IgG. Values are means±s.d. (n=4). (b) Scheme for full-length TRA2β4 bearing bacteriophage MS2 hairpins (pMS-TRA2β4). YFP, yellow fluorescence protein. (c) After HCT116 cells were co-transfected with pMS2-YFP and pMS-TRA2β4 or control mock (pMS), association between Sp1 and TRA2β4 was analyzed using immunoprecipitaion with anti-YFP antibody and western blotting with anti-Sp1 antibody. (d) Nuclear fractions (40 μg) prepared from HCT116 cells were incubated with 1 μg of biotinylated transcripts designed as exon 1 (ex1), exon 2 (ex2) and exon 3 (ex3) of TRA2β4 in 10 mm Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0, containing 1 mm EDTA, 250 mm NaCl and 0.5% Triton X-100 for 1 h at room temperature. RNA–protein complexes were isolated with paramagnetic streptavidin-conjugated Dynabeads, and bound Sp1 was detected by western blotting. (e) Nucleotide sequence of TRA2β4 exon 2. Two consensus Sp1-binding sites are boxed. Formation of stem-loop structure of TRA2β4 exon 2 RNA (449–488 nt) and its disruption by the mutation of 485-GGGG-488 to 485-AAGG-488 are shown below. These structures were predicted using CentroidFold and M-FOLD programs. (f) Scheme for pMS2-LUC (Renilla luciferase gene (LUC)), pMS2-LUC-exon 2 wild-type (pMS-ex2 wt), pMS2-LUC-exon 2 mt-1 (pMS-ex2mt-1), and pMS2-LUC-exon 2 mt-2 (pMS-ex2mt-2). Arrows indicate a primer set used. (g and h) Nuclear lysates prepared from UV-crosslinked HCT116 cells were subjected to an RIP assay using an anti-Sp1 antibody. Immunoprecipitated LUC-fused exon 2 RNAs were measured by qPCR. Data are shown as enrichment relative to values obtained from amount of each input. Values are means±s.d. (n=4).