Fig. 6.
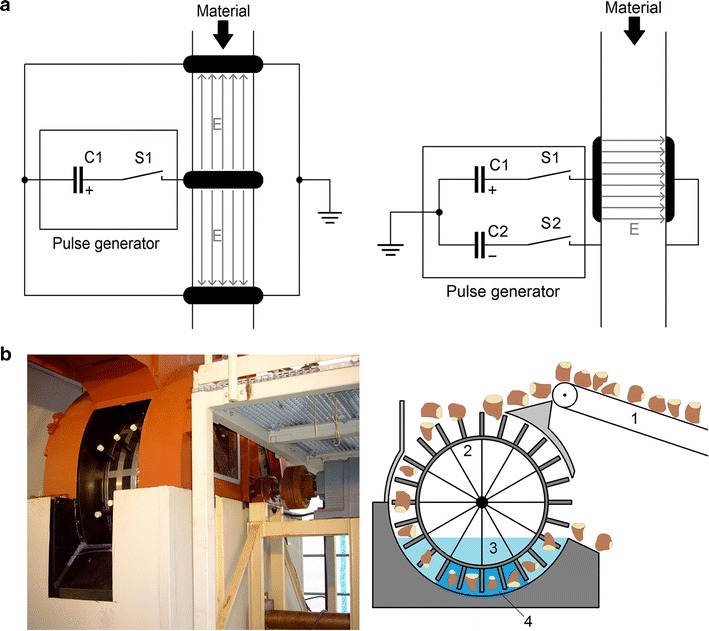
a PEF treatment reactor with collinear (left panel) and parallel plate (right panel) electrode arrangement each connected to a pulse generator. The material is transported through the electrodes and tubes passing two treatment areas between high-voltage- and ground electrodes. The electric field is oriented either in direction or counter direction of the material flow. In the parallel plate electrode arrangement, the orientation of the electric field is perpendicular to the material flow. The electrode system is fed symmetrically to ground potential by a pulse generator grounded at its center point. Hence, in a substantially homogeneous medium, ground potential is established in the center of the electrode system preventing leakage currents from flowing out of the electrode system toward inlet and outlet. b PEF treatment reactor for whole sugar beets developed by KIT/IHM (digital image, left panel and schematic representation, right panel): The sugar beets are transported by means of a conveyor belt (1), to the top of a wheel equipped with electrically isolating rods (2), when rotating the wheel the rods transport the sugar beets as a package through the PEF treatment reactor. The beets are immersed into water (3), to establish an electric contact to the electrodes situated inside the PEF treatment area (4)
