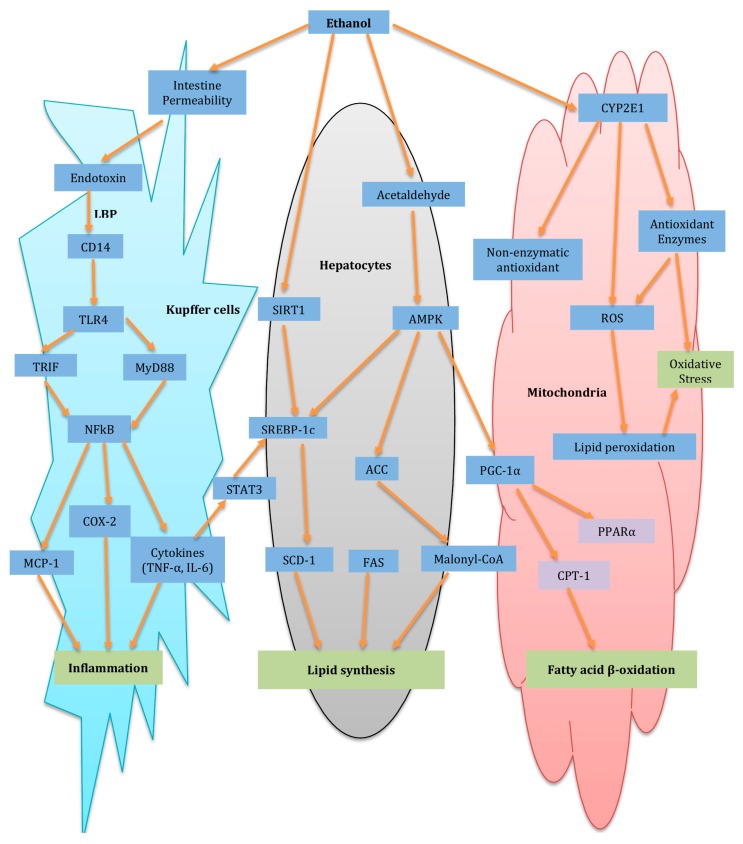
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of major pathways of alcoholic fatty liver (ALD) and potential molecular targets of herbal medicine for the protection of ALD. The arrows indicate the potential molecular targets involved in the development of ALD and regulated by herbal medicines. ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CD14: cluster of differentiation 14 COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; CPT-1: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1; CYP2E1: Cytochrome P450 2E; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; IL-6: Interleukin 6; MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor g coactivator α; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor RNS Reactive nitrogen species; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SCD-1: Stearyl CoA desaturase-1; SIRT1: Sirtuin 1; SREBP-1c: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c; STAT-3: signal transducer and activator of transcription-3; TLR: Toll-like receptor 4; TRIF: TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-b; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.