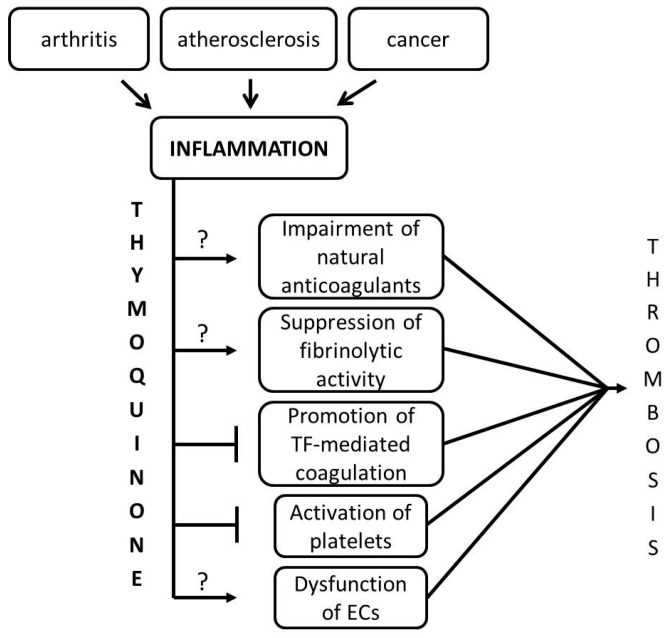
Figure 6.
THQ interferes with the crosstalk between inflammation and thrombosis. Inflammation is triggered under various pathophysiological conditions in the body such as arthritis, atherosclerosis, and cancer. An increase in blood coagulation or thrombosis is seen in all of these conditions. Inflammation-triggered cytokines, particularly TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, enable a cascade of events, culminating in thrombosis. We provide evidence in this study that THQ can effectively inhibit tissue factor (TF)-mediated coagulation and inactivation of platelets that lie in the crosstalk between inflammation and thrombosis. The effect of THQ on natural anticoagulants, endothelial cells (ECs), and fibrinolytic activity could not be investigated in this study due to limitations of the in vitro system; this is represented by ‘?’. In addition, THQ also exerts an effect, although moderate, on the factor Xa activity of the blood coagulation system.