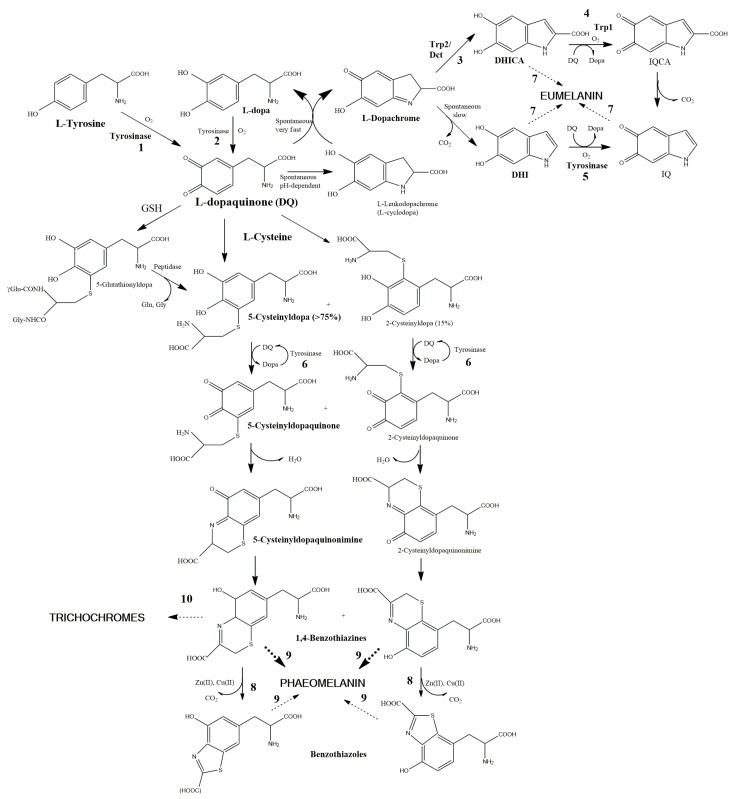
Figure 1.
Melanogenesis pathway. l-Ty is oxidized to l-dopaquinone by tyrosinase. l-dopaquinone is a branch point to eumelanogenesis (internal cyclization to indole, the classical Raper–Mason pathway) or pheomelanogenesis (thiol addition on the aromatic ring). Other reactions lead to dark eumelanin (upper part) or yellowish to reddish pheomelanin (lower part). Enzymatic-catalyzed reactions are numbered 1–6, and metal ions l-catalyzed reactions are numbered 7–10, although traces of those metal ions can replace tyrosinase and Trps at reactions 2–6. Reaction 1 is the only key and rate-limiting step of the pathway. Mammalian and avian melanogenesis do not show differences concerning this essential step, but the availability of metal ions to catalyze rearrangements at the final steps may show differences among mammalian skin and avian feathers. See text for other details.