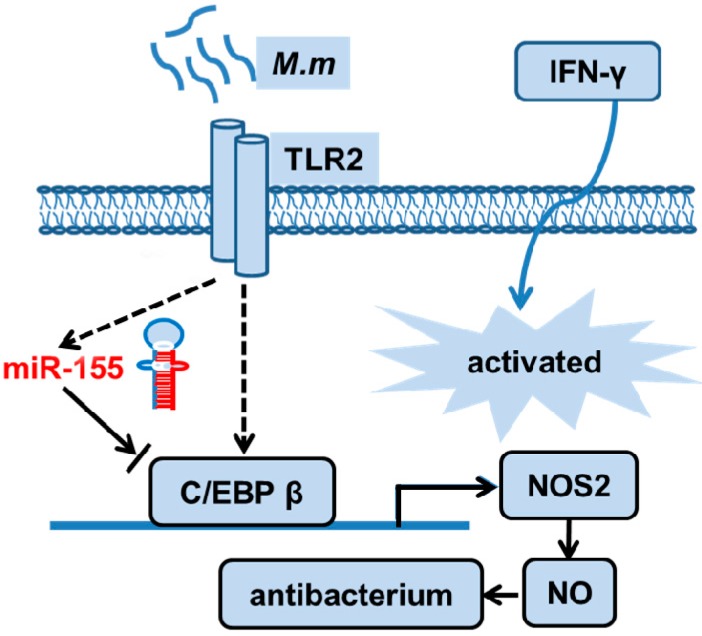
Figure 6.
Schematic outline of miR-155-regulated bactericidal activity. miR-155 expression is induced by M.m in IFN-γ activated macrophages and mediates translational inhibition of C/EBPβ by targeting its 3′UTR. Successively, C/EBPβ is induced and mediates NO-dependent antibacterial mechanism. Thereby, miR-155 can negatively regulate the NO-dependent antibacterial mechanism by C/EBPβ. Black dash line arrow: direct effect; black solid line arrow: indirect effect; blue arrow: activated.