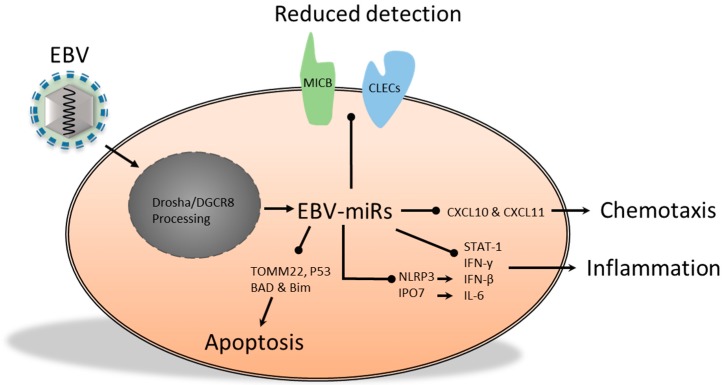
Figure 2.
EBV miRs can alter the expression of multiple proteins, cytokines and chemokines in various cell types. These alterations may benefit pathogen persistence by affecting key pro-inflammatory processes, such as: detection by natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), cytokine signaling, chemotaxis and apoptosis. MICB, CLECs, CXCL10, IPO7, Bim and TOMM22 have been verified as vmiR targets by reporter assays and PAR-CLIP analysis, while CXCL11, P53, BAD and NLRP3 have only been verified by reporter assays. MICB, MHC class I-related chain B; CLECs, C-type lectin domain family members; DGCR8, DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8; TOMM22, translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 22 homolog; STAT, signal transducers and activators of transcription; BAD, Bcl-2-associated death promoter; Bim, Bcl-like protein 11; IPO7, importin 7; CXCL, chemokine (C–X–C motif) ligand; NLRP3, NLR family, pyrin domain containing 3.