Table 1.
Representative flavonoids showing anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects.
| Name of Flavonoids | Structures | Plant Sources | Anti-Obesity and Anti-Diabetic Effect in in Vitro/in Vivo Model | Molecular Mechanism in Obesity and Diabetes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 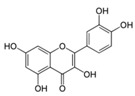 |
Apples, berries, red onions, cherries, broccoli, coriander, etc. | ↑ Apoptosis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes | ↓ PARP, ↑ AMPK, ↑ Caspase 3 and 9 |
[45] |
| ↑ Glucose uptake in rat adipocyte, C2C12 muscle cells | ↑ GLUT4 | [46] | |||
| ↑ Glucose uptake, ↓ Fat accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes |
↓ PPARγ1 | [47] | |||
| ↓ Hyperglycemia, ↑ Insulin in STZ-induced diabetic rats, db/db mice |
↓ NF-κB, ↓ Caspase 3, ↓ MDA levels, ↑ SOD and CAT |
[48] | |||
| Rutin | 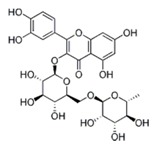 |
Buckwheat, oranges, grapes, lemons, limes, peaches and berries | ↓ Blood lipids, ↓ Fatty liver in DIO mice and rat |
↓ PPAR and ↓ C/EBP, ↓ TNF-α, ↓ IL-6 |
[49] |
| ↑ Glucose uptake in the rat soleus muscle | ↑ PI3K, ↑ MAPK |
[50] | |||
| Isorhamnetin | 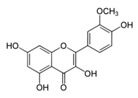 |
Ginkgo biloba L., Hippophae rhamnoides L. and Oenanthe javanica (Blume) | ↓ Hyperglycemia and oxidative stress in STZ-induced diabetic rat, Inhibition adipogenesis in 3 T3-L1 cells | ↓ PPARγ, ↓ C/EBPα |
[51] |
| ↑ Insulin secretion in HFD-induced C57BL/6 mice | ↑ GLUT2, ↑ PPARγ |
[52] | |||
| Kaempferol | 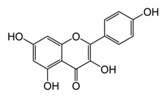 |
Grapefruit, tea, cruciferous vegetables | ↓ Hyperglycemia, ↑ Glucose uptake in rat soleus muscle |
↓ Caspase 3 | [53] |
| ↑ β-cell survival in INS-1E cells | ↑ GLUT4, ↑ AMPK |
[54] | |||
| ↑ Antioxidant defense and body weight gain in diabetic rats and HFD-obese mice | ↓ PPARγ, ↓ SREBP-1c, ↓ TNF-α, ↓ IL-6 |
[55] | |||
| Resveratrol | 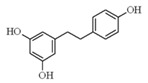 |
Red grapes, red wine, peanuts, and ground nuts | ↑ Glucose uptake | ↑ GLUT4 | [56] |
| ↓ Lipid accumulation 3T3-L1 | ↓ PPARγ | [57] | |||
| ↑ Lipolytic activity in adipocytes | ↑ cAMP | [58] | |||
| Naringenin | 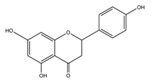 |
Spreng, Grapefruits, oranges and tomatoes | ↓ Blood lipids, ↓ Fatty liver in Hypercholesterolemic rats |
↓ HMG-CoA, ↓ ACAT |
[59] |
| ↓ Glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes | ↓ PI3K, ↓ AKT |
[60] | |||
| ↓ Hyperglycemia in STZ-induced rat | ↑ Antioxidant enzyme (SOD) | [61] | |||
| Naringin | 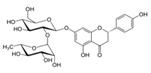 |
Citrus fruits and Grapefruit | ↓ Hyperglycemia, ↑ Plasma insulin, ↑ Leptin in STZ-induced diabetic mice and db/db mice |
↑ GLUT4, ↑ PPARγ |
[59] |
| ↓ Blood lipids, ↓ Fatty liver in db/db Mice |
↓ HMG-CoA, ↓ ACAT |
[62] | |||
| Hesperidin | 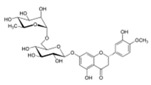 |
Lemons and oranges | ↓ Blood glucose level, ↓ Blood lipids in STZ-induced type 1 diabetic rats |
↑ Glucokinase | [63] |
| ↓ Oxidative stress, apoptosis | ↑ GLUT4, ↓ HMG-CoA, ↓ ACAT |
[64] | |||
| Eriodictyol | 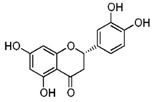 |
Lemon fruits | ↓ Adipocyte-specific fatty acid binding protein in differentiated 3 T3-L1 adipocytes | ↑ PPARγ | [65] |
| ↑ Glucose uptake, ↑ Insulin resistance in HepG2 cells |
↑ AKT | [65] | |||
| ↓ Diabetes-related lipid peroxidation | ↓ TNFα, ↓ ICAM-1, ↓ VEGF |
[66] | |||
| Genistein | 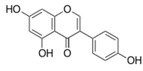 |
Soy foods | ↓ Plasma triglycerides in Sprague-Dawley rats | ↑ GLUT4 | [67,68,69] |
| ↑ Insulin-positive β cell in HG-induced diabetic mice | ↑ cAMP signaling, ↑ PKA activation |
[70] | |||
| ↓ Blood glucose, ↓ Blood HbA1c in STZ-induced diabetic mice, ↓ Adipocyte differentiation |
↓ TNF-α, ↓ TGFβ1, ↓ NF-κB, ↑ AMPK, ↑ ACC |
[71] | |||
| Daidzein | 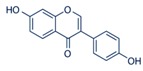 |
Soy foods and nuts | ↓ Blood glucose, ↓ Urinary glucose |
↓TNF-α, ↓ TGFβ1, ↓ NF-κB |
[70] |
| ↓ Plasma triglycerides in Sprague-Dawley rats | ↑ GLUT4, ↓ G6Pase, ↓ PEPCK |
[67] | |||
| Apigenin | 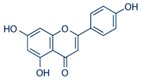 |
Passion flower and chamomile | ↓ Hyperglycemia, ↓ Oxidative stress in STZ-induced diabetic rats and mice |
↓ NF-κB, ↓ TNF-α, ↓ IL-1β |
[72] |
| ↑ Glucose uptake, ↑ Insulin secretion in alloxan-induced diabetic mice and INS-1E cells, ↓ Lipid accumulation, ↓ Hyperglycemia in HepG2 hepatocytes |
↓ G6Pase, ↑ GLUT4, ↑ AMPK, ↓ MCP-1, ↑ AMPK, ↑ ACC |
[73] | |||
| Luteolin | 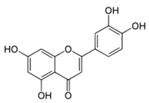 |
Celery, parsley, broccoli, onion leaves, carrots, peppers, cabbages, apple skins, and chrysanthemum flowers | ↑ Insulin secretion in 3T3-L1 hepatocyte | ↑ GLUT4, ↑ Leptin |
[74] |
| ↑ Insulin secretion in uric acid damaged pancreatic β-cells | ↓ MAFA, ↓ NF-κB, ↓ CREB-B |
[75] | |||
| Tangeretin | 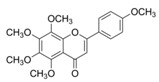 |
Citrus fruit rinds, mandarin orange | ↑ Insulin secretion, ↑ Glycogen, ↓ Total cholesterol in HFD-induced obese mice |
↓ TNF-α, ↓ IL-6, ↓ IL-1β |
[76] |
| ↓ Plasma glucose level, ↓ Plasma HbA1c in diabetic rats |
↑ AMPK | [77] | |||
| Epicatechin Gallate | 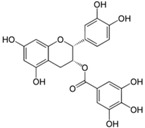 |
Tea, grapes and seeds of certain leguminous plants | ↓ Hepatic lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells | ↓ Fatty acid synthase, ↓ ACC1 |
[78] |
| (−)-Catechin | 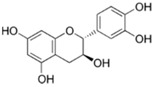 |
Tea, grapes and seeds of certain leguminous plants | ↓ Insulin-dependent glucose uptake, ↑ Adiponectin protein |
↓ KLF7, ↓ PPARγ, ↓ C/EBPα |
[79] |
| (−)-Epigallo catechin gallate | 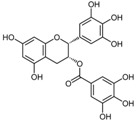 |
Tea, grapes and seeds of certain leguminous plants | ↑ Insulin secretion, protect insulin-producing β-cells | ↑ FOXO1, ↑ PDX-1, ↑ IRS2, ↑ AKT, ↑ NeuroD, ↑ MAFA |
[80] |
| Cyanidin | 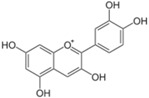 |
Plants with purple corn color (PCC) | ↓ White and brown adipose tissue weights, ↓ Hyperglycemia |
↓ TNF-α, ↓ SREBP-1 |
[81] |
| Anthocyanins | 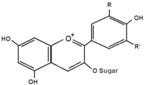 |
Black soybean seed coats bilberries | ↓ Hyperglycemia, ↑ Insulin sensitivity, ↑ GLUT4 (WAT and muscle) in T2DM mice |
↑ AMPK, ↓ PEPCK, ↓ G6Pase, ↓ ACC1, ↓ PPARα, ↑ Acyl-CoA oxidase, ↑ CPT-1A, ↓ RBP4 |
[82] |
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside | 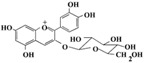 |
Plant bayberry fruit | Protect hepatocytes ↓ HG-stimulated damage |
↑ AKT, ↓ JNK, ↓ TNF-α, ↓ IL-6, ↓ MCP-1 |
[83] |
| ↑ Insulin secretion in oxidative stress-induced pancreatic β damage | ↑ GLUT4, ↑ LPL, ↑ FAS, ↑ AMPK |
[84] |
(↓) Decrease, (↑) Increase.
