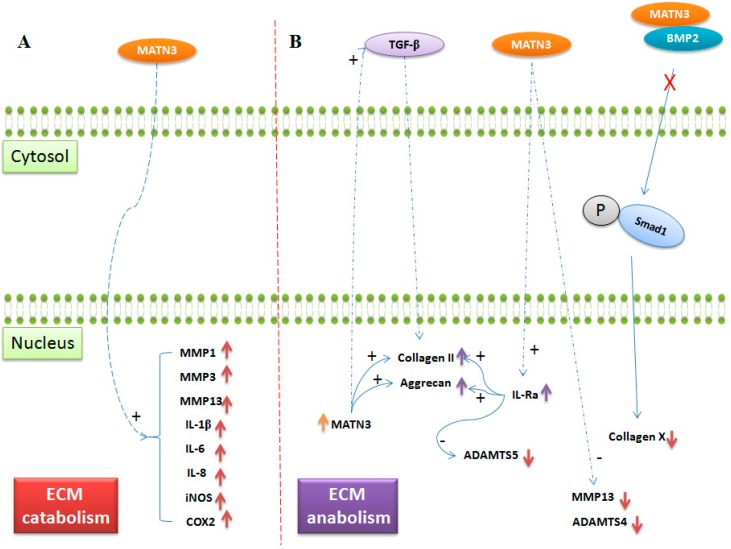
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram illustrates the role of matrilin-3 in ECM modulation of cartilage. (A) ECM catabolism: Matrilin-3 at supra-physiological concentrations (~5 to 50μg/mL) increases MMP1, MMP3, MMP13, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, iNOS, and COX2 expression in chondrocytes (red upward arrows); (B) ECM anabolism and hypertrophy: Matrilin-3 mediates the TGF-β signaling pathway. The overexpression of matrilin-3 (orange upward arrow) increases collagen II and aggrecan expression. Matrilin-3 at low concentrations (~100 to 200 ng/mL) increases IL-Ra expression, which increases collagen II and aggrecan expression (purple upward arrows), and reduces ADAMTS5. Recombinant matrilin-3 reduces ADAMTS4 and MMP13 expression (red downward arrows). Matrilin-3 binds to BMP2, thereby inhibiting BMP downstream signaling, collagen X expression, and chondrocyte hypertrophic differentiation (red cross in B). Abbreviations: ECM, extracellular matrix; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; IL, interleukin; iNOS, induced nitric oxide synthase; COX2, cyclooxygenase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; IL-Ra, Interleukin receptor antagonist; ADAMTS, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein. Dashed arrows (blue), unidentified signaling pathways; solid arrow (blue), identified signaling pathway; (+), positive regulatory effect; (−), negative regulatory effect.