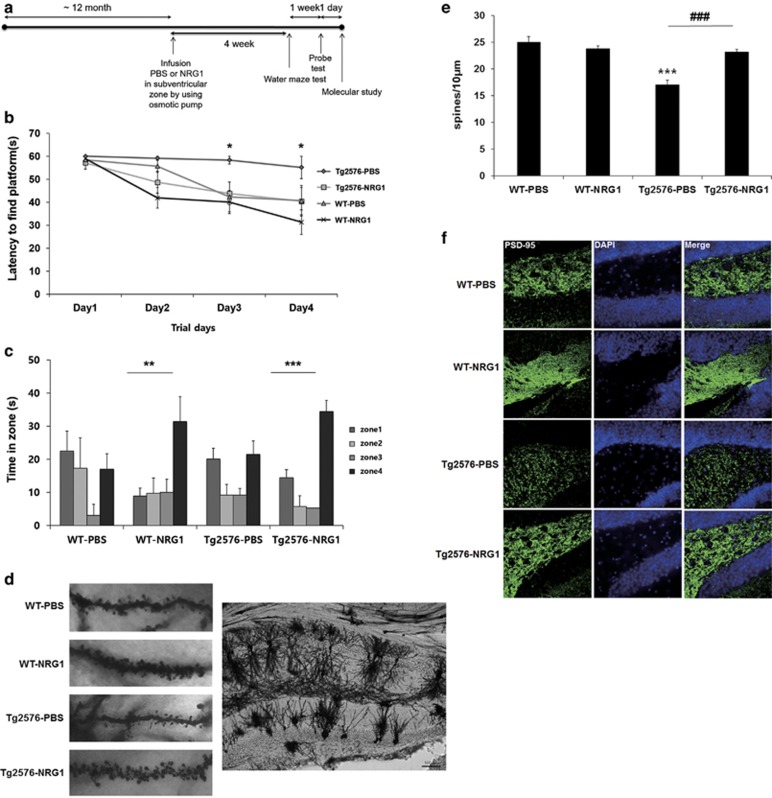
Figure 1.
Intraventricular infusion of NRG1 peptide attenuates learning and memory deficits in Tg2576 mice. (a) An experimental schematic of intraventricular infusion of NRG1 peptide using an osmotic pump is shown. PBS or NRG1 was infused into 12-month-old Tg2576 mice and their WT littermates. The Morris water maze test was performed 4 weeks after the osmotic pump insertion surgery. (b) Animals were required to find a submerged platform (12 cm in diameter, 35 cm in height) in the pool using spatial cues. Three training trials per day were conducted for four consecutive days, in which the initial placement of the mice into the maze was changed for trial and for each group. The latency to escape to the hidden platform was recorded for each training session. Significant differences were detected between the Tg2576-PBS group and the Tg2576-NRG1 group on day 3 and day 4 of the Morris water maze task. (n=5 for WT-PBS, 6 for WT-NRG1, 3 for Tg2576-PBS and 4 for Tg2576-NRG1) per group; *P<0.05 based on a one-way ANOVA, post hoc analysis Fisher's LSD. (c) Forty-eight hours after the final trial session, a single probe trial was conducted. The escape platform was removed, and each mouse was allowed to swim for 60 s in the maze. NRG1-infused WT or Tg2576 mice remained significantly longer in zone 4 than the remaining zones (zones 1, 2 and 3) (one-way ANOVA, **P<0.01, **P<0.001). (d) Golgi-Cox staining was performed on the mouse brains using a FD Rapid GolgiStain Kit (FD Neuro Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Right; a representative image of CA1 subregion of hippocampus from WT-PBS-infused mice. Left; representative images of dendritic spines are provided for the WT-PBS, WT-NRG1, Tg2576-PBS and the Tg2576-NRG1-infused mice. (e) For each group, two to three brains from each group were subjected to Golgi-Cox staining (WT-PBS: n=3, WT-NRG1 n=2, Tg2576-PBS n=2, Tg2576-NRG1 n=2). Pyramidal neurons with countable morphology in the CA1 region were selected from the slides (WT-PBS: n=23, WT-NRG1 n=14, Tg2576-PBS n=11, Tg2576-NRG1 n=16), and two to four dendrites were counted to score each neuron). Tg2576 mice exhibited a reduced dendritic spine density compared with WT mice (WT-PBS: 25.03±1.04 spines/10 μm, n= 23; Tg2576-PBS: 17.06±7.09 spines/10 μm, n=11, ***P<0.001). NRG1 infusion in Tg2576 mice alleviated the decrease in dendritic spine density in the CA1 region (23.24±0.44, n=16, ***P<0.001 compared with Tg2576-PBS). (f) Representative images displaying the immunoreactivity against PSD95 for the four groups. Representative images were selected in a blinded manner