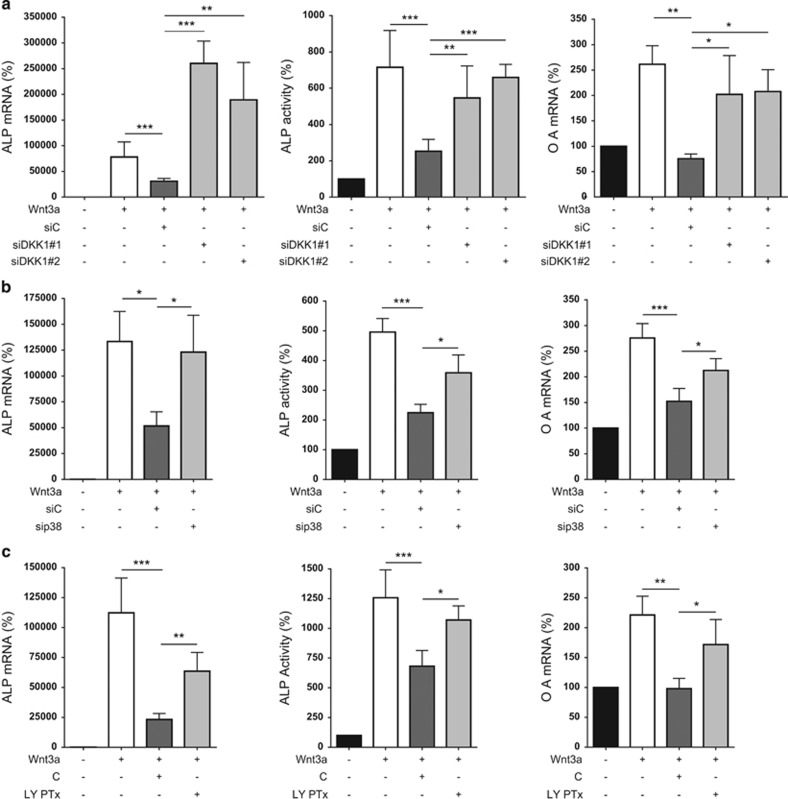
Figure 5.
Regulating PC3-derived DKK-1 has reversal effects on suppressed osteoblastogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells. (a) Transient knockdown of DKK-1 in PC3 cells was achieved using two different siRNAs. The supernatant of transfected cells was removed and supplemented with fresh medium 24 h post transfection. Supernatants used in experiments were then collected 48 h later. Control siRNA (siC) and two DKK-1 siRNA PC3 supernatant (siDKK-1#1 and #2) (15%) were used to treat C2C12 cells in combination with Wnt3a-containing L-cell media (10%) and 5% FCS DMEM/F-12 (75%) for 72 h. Ten percent L-cell was used in the control conditions and 200 ng/ml BMP-2 was supplemented to all conditions. ALP and osteoactivin (denoted OA) mRNA expression levels were then assessed by qRT-PCR and ALP activity by enzymatic assay. (b) DKK-1 expression was suppressed indirectly by combination knockdown of p38 MAPKs in PC3 using siRNAs directed against MAPK11, MAPK12 and MAPK14. PC3 supernatant was harvested and used to treat C2C12 cells as previously detailed (siC=si control RNA and sip38=siRNA combination of the three p38 MAPK isoforms). Assessment of ALP mRNA expression, ALP activity and osteoactivin mRNA expression was then performed. (c) DKK-1 expression was suppressed using the p38 MAPK inhibitor LY2228820. PC3 cells were pre-treated with the inhibitor (10 μM) for 6 h before performing a fresh medium change and collecting supernatant 18 h later (LY PTx). These supernatants were then used to treat C2C12 cells as detailed previously (C=control PC3 supernatant). ALP mRNA expression, ALP activity and osteoactivin mRNA expression levels were then analyzed. mRNA expression data of N≥3 are shown as a percentage of the control L-cell treatment and results are shown as the mean±S.D. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001)