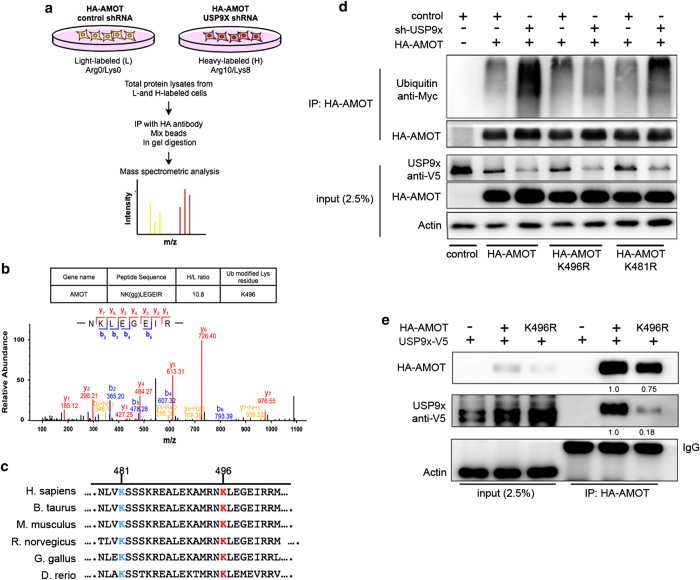
Figure 4.
K496 is required for USP9x activity on AMOT. (a) Design of the SILAC-based mass spectrometry experiment to detect ubiquitylation sites in AMOT. (b) Annotated tandem mass spectrum of ubiquitylated (di-Gly modified) peptide corresponding to AMOT K496. (c) Sequence alignment of the region of AMOT containing residues K481 and K496 from the indicated species. (d) Immunoblots of HEK293T cells transfected to express HA-tagged AMOT p130 with Myc-tagged Ubiquitin and shRNA vectors to deplete USP9x or control shRNAs. Three forms of HA-AMOT were tested: native, K496R and K481R mutant. Cells were treated with MG132. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA to recover AMOT and blots were probed to detect Ubiquitin (anti-Myc), AMOT (anti-HA) or with anti-Actin to control for loading. Anti-USP9x was used to show the efficiency of shRNA-mediated depletion in the total cell lysate. (e) Immunoblots of HEK293T cells transfected to express HA-tagged native AMOT or K496R mutant AMOT together with V5-tagged USP9x. Cells were treated with MG132 before harvesting cell lysates for immunoprecipitation with anti-HA. Blots were probed with anti-HA to detect AMOT and with anti-V5 to detect USP9x. The HA-AMOT and V5-USPx bands were analyzed using Image J (www.NIH.GOV) and the values are shown below, with the AMOT-K496R mutant lane normalized to the adjacent native AMOT lane. K496R AMOT expression was somewhat lower than the native protein, as shown in the total lysate panel (at left).