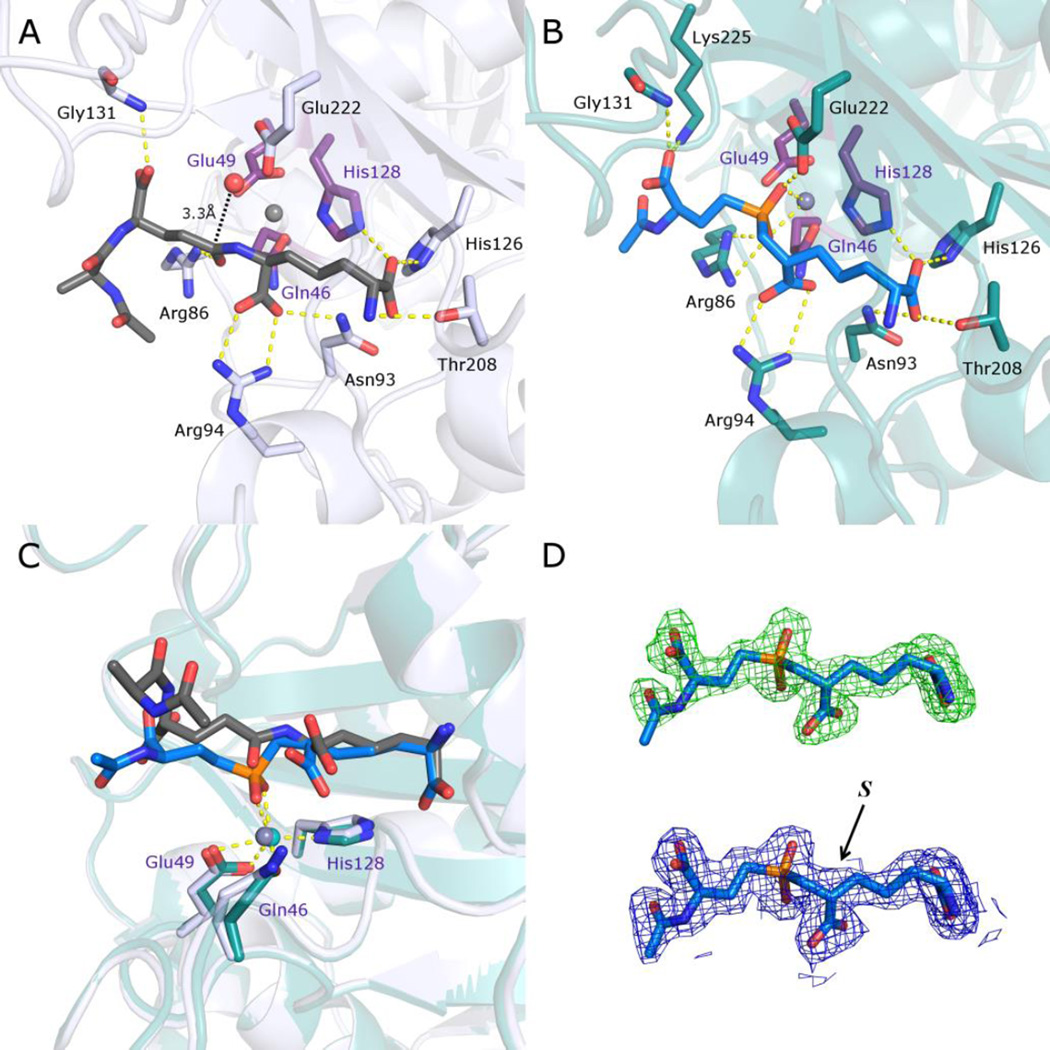
Figure 2.
Comparison of structures of Csd4 in complex with a N-acetyltripeptide substrate and inhibitor 1. A) The structure of N-acetyltripeptide complexed with Csd4 (produced using PDB ID: 4WCN). The substrate carbon atoms are in dark grey; selected Csd4-substrate interactions are shown as yellow dotted lines; zinc ligands are colored purple; carbon atoms of residues interacting with the tripeptide are colored white; the predicted catalytic water is red; zinc is grey. B) Structure of the Csd4-inhibitor 1 complex. The bound inhibitor (carbon atoms in blue) with key active site residues are highlighted. Carbon atoms of selected amino acid residues that interact with the inhibitor are shown in teal. C) Superposition of the structures of Csd4 with bound substrate and inhibitor 1. The substrate, inhibitor 1 and zinc ligands are shown as in panels A and B. D) Top, the initial omit Fo−Fc map contoured at 3.5 σ prior to modelling of the inhibitor, and below, the final refined 2Fo−Fc map of the inhibitor contoured at 1.5 σ. In both maps, the final refined inhibitor model is included for visualization purposes. The (S)-configuration of the inhibitor stereocenter that is closest to the phosphinate is labeled. In all panels, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus atoms are shown in red, blue and orange, respectively.