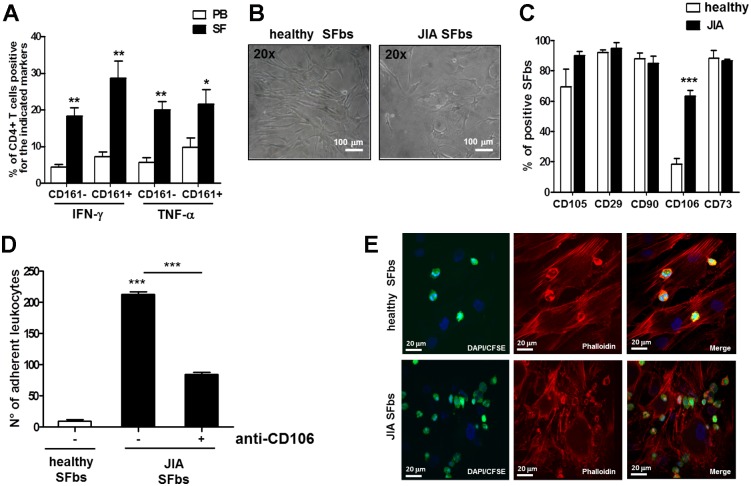
Fig 4. SFbs derived from synovial fluid of JIA patients express higher level of CD106 than normal SFbs.
A. MNCs from PB and SF of JIA patients were polyclonally stimulated with PMA plus ionomycin for 6h the last 4h in presence of BFA and then evaluated for intracellular cytokines production. Columns represent mean ± SE of % of CD3+CD4+ T cells of seven JIA patients producing the indicated cytokine and expressing CD161. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 PB versus SF; B SFbs obtained from healthy subjects and from SF of JIA patients were evaluated by phase contrast microscope (magnification 200X, one representative experiment out of seven and of this one field out of five is shown, scale bar = 100 μm and (C) were characterized by flow cytometry for surface expression of CD106, CD29, CD90, CD106, CD73. Columns represent the mean ± SE of % of SFbs from six healthy donors and from seven JIA patients positive for the indicated markers. *** p < 0.001 JIA versus healthy SFbs; D-E CFSE-labelled leukocytes derived from PB of healthy donors were cultured for 2h on healthy- or JIA-derived SFbs, in presence or absence of anti-CD106 neutralizing mAb. Leucocytes adhesion on SFbs was evaluated by fluorescence microscope analysis by average of adherent leucocytes counted in five different random fields (D, columns represent mean ± SE of number of adherent leukocytes of three different experiments, *** p < 0.001 stimulated condition versus ctrl or indicated by bar) and by confocal microscopy analysis (E, magnification 400x, one representative experiment out of three and of this one field out of five is shown). Statistical analysis was performed by using the Student t-test (two groups) or the ANOVA test (several groups).