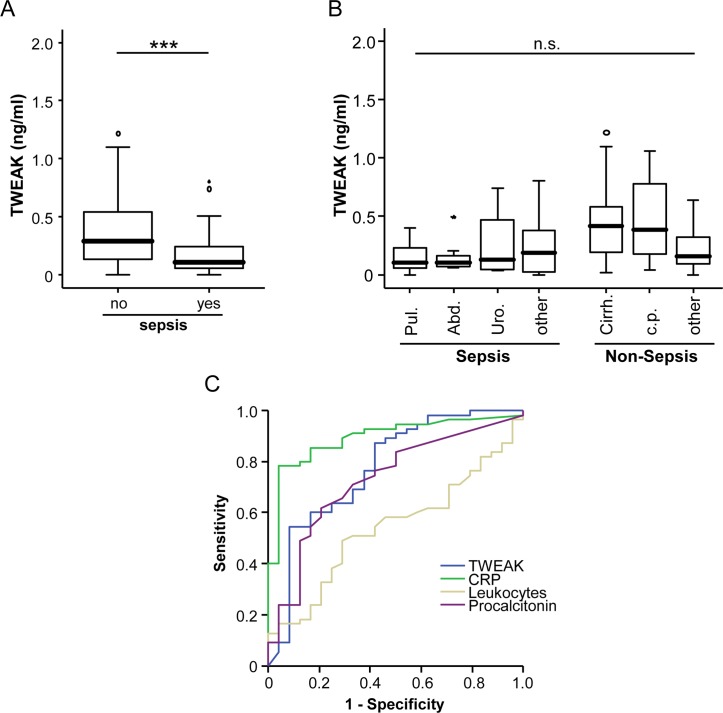
Fig 2. Serum TWEAK concentrations are decreased in sepsis.
(a) Critically ill patients with sepsis (n = 84) displayed significantly lower TWEAK serum concentrations (n = 37, U-test) compared to patients without sepsis. (b) TWEAK serum concentrations were not different in patients with different etiologies of critical illness and are highest in patients with cardiac diseases. (c) ROC curve analyses comparing the diagnostic power in predicting sepsis of TWEAK with well-established laboratory markers: C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin, and white blood cell count (leukocytes).