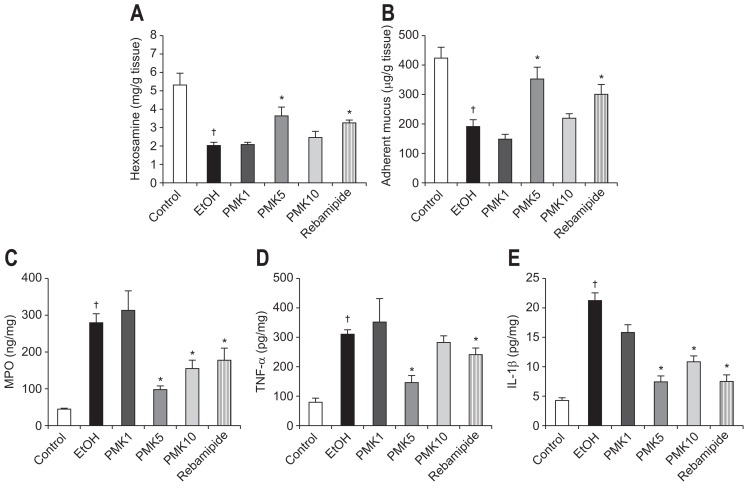
Fig. 2.
Gastric mucus levels and anti-inflammatory activities of PMK-S005 in ethanol-induced gastric damage. Hexosamine concentrations (A) and adherent mucus (B) were significantly decreased after the intragastric administration of ethanol, and these reductions were markedly relieved by pretreatment with 5 mg/kg of PMK-S005. The ethanol-administered rats showed marked increases in myeloperoxidase (MPO) (C), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) (D), and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) levels (E). These increases were significantly inhibited by pretreatment with 5 mg/kg PMK-S005. The results are expressed as the mean±SEM from five to 10 animals per group. *p<0.05 compared with the ethanol group; †p<0.05 compared with the control group.