Fig. 4.
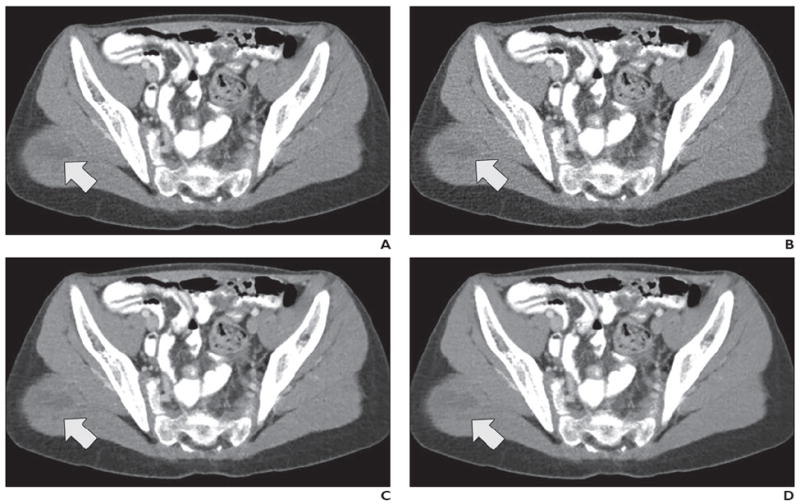
12-year-old boy with metastatic Wilms tumor in right gluteal muscle (arrow). After undergoing left nephrectomy for resection of Wilms tumor, patient underwent contrast-enhanced abdominopelvic CT performed to evaluate postoperative changes.
A–D, CT images shown compare four dose plus reconstruction settings: full dose plus filtered back-projection (FBP) (A), half dose plus FBP (B), half dose plus sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction (SAFIRE, Siemens Healthcare) (C), and half dose plus adaptive nonlocal means (aNLM) (D). Scanning parameters included kilovoltage of 120 kV and full-dose volume CT dose index of 5.8 mGy. Half dose was 2.9 mGy. All three readers ranked half dose plus aNLM images higher than original full-dose images. Average scores from all three readers for four images were as follows: 4.3 for full dose plus FBP, 3.0 for half dose plus FBP, 4.0 for half dose plus SAFIRE, and 4.3 for half dose plus aNLM.
