Figure2.
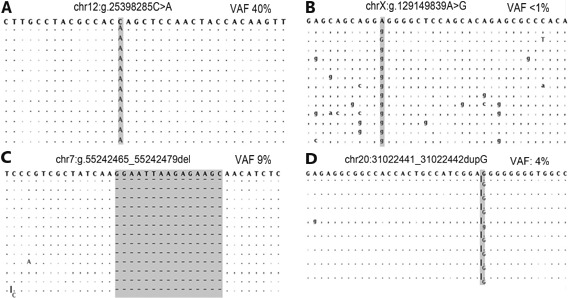
Alignment views of four variants detected by NGS. Each panel depicts a representative set of variant reads for single nucleotide variant (A and B) or insertion/deletion variants (C and D) with either high quality (A and C) or low quality (B and D). The human genome reference sequence is the string of bases along the top of each panel. Aligned basecalls matching the reference are listed as dots (plus strand) or commas (minus strand). High quality variants typically have higher variant allele frequencies (VAF), and variants reads have fewer additional variants. Panel D depicts known false positive locus, likely due to the "homopolymer problem" where certain NGS technologies overcall insertion/deletion variants where the reference sequence has five or more of the same nucleotides in a row (in this case, 8 guanines).
