Figure 2. hERG cellular processing .
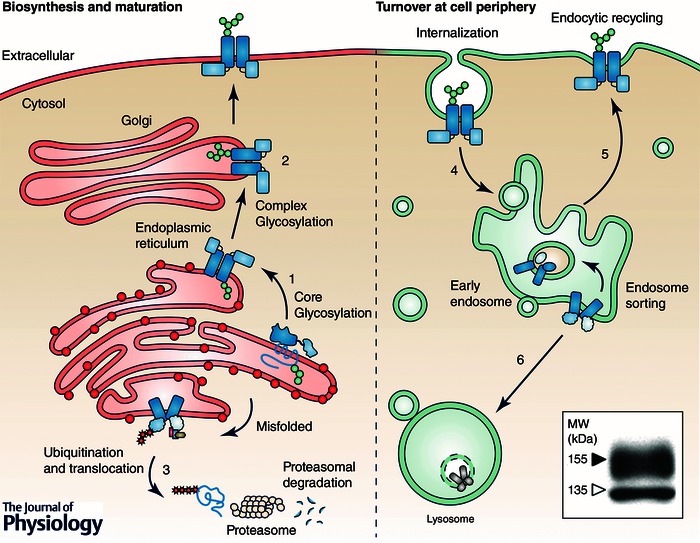
Overview of hERG cellular processing. Nascent channels are cotranslationally inserted into the ER membrane (1) where they undergo N‐linked glycosylation to an apparent molecular mass of 135 kDa. Upon proper folding and assembly, hERG is exported to the Golgi where it is subject to additional glycosylation, increasing the apparent molecular mass to 155 kDa prior to export to the plasma membrane (2). Nascent channels, which fail to fold at the ER, are targeted for proteasomal degradation (3). PM‐resident hERG is internalized (4) and either recycled back to the PM (5) or targeted for lysosomal degradation (6). Inset, typical immunoblot of WT hERG. Indicated are the immature 135 kDa core‐glycosylated and mature 155 kDa complex glycosylated forms (open and filled arrow respectively). hERG is detected in stably transfected HeLa cells by immunoblotting against an engineered HA‐epitope in the S1–S2 extracellular loop (Ficker et al. 2003).
