Figure 1. CORD7 mutation R655H affects regulation of Cav2.1 channel inactivation by RIM1 via β association.
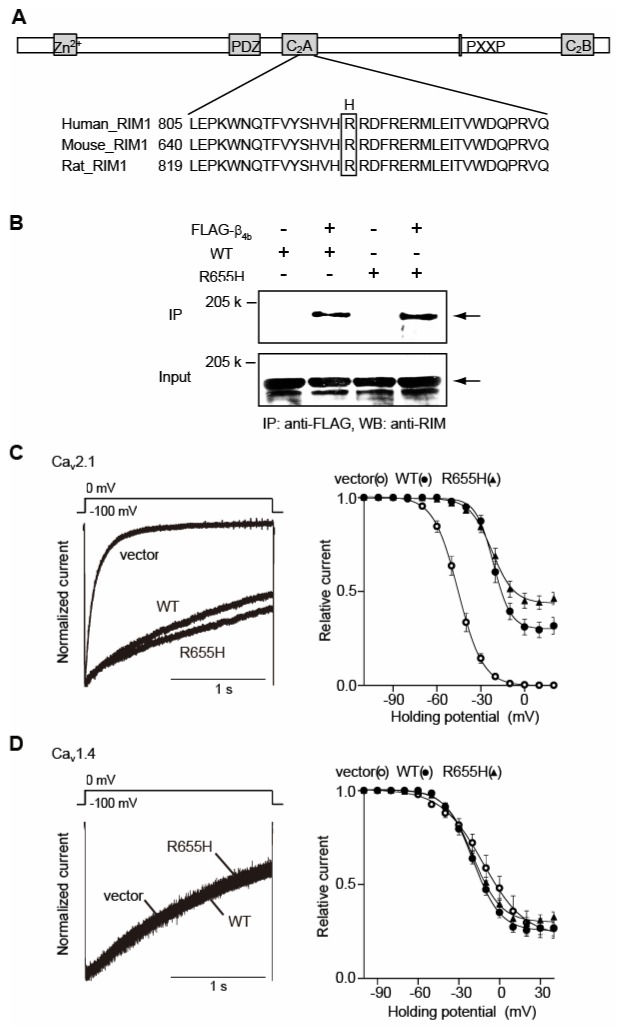
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of C2A domains of human, mouse and rat RIM1. The position of the CORD7 substitution (H) is indicated. (B) Physical association of recombinant β4b and RIM1 mutant in HEK293 cells. The interaction is evaluated by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody, followed by western blotting (WB) with anti-RIM antibody. Left panel: co-immunoprecipitation of wild-type RIM1 (WT) with FLAG- β4b. Right panel: co-immunoprecipitation of R655H with FLAG-β4b. (C) Effects of WT and R655H on the inactivation properties of P/Q-type Cav2.1 currents in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. Left panel: inactivation of P/Q-type Cav2.1 currents. The peak amplitudes are normalized for Ba2+ currents elicited by 2-s pulses to 0 mV from a holding potential (Vh) of −100 mV before and after expression of WT or R655H. Right panel: inactivation curves of P/Q-type Cav2.1 currents in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. The voltage dependence of inactivation, determined by measuring the amplitude of the peak currents evoked by 20-ms test pulses to 0 mV following 2-s prepulses to potentials from −100 to 20 with increments of 10 mV from a Vh of −100 mV, was fitted with the Boltzmann’s equation. (D) Effects of WT and R655H on the inactivation properties of L-type Cav1.4 currents in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. Left panel: inactivation of L-type Cav1.4 currents. Right panel: inactivation curves of L-type Cav1.4 currents in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. The voltage dependence of inactivation, determined as in (C) above.
