Figure 2. CORD7 mutation R655H affects regulation of Cav1.4 channel activation by RIM1 via β association.
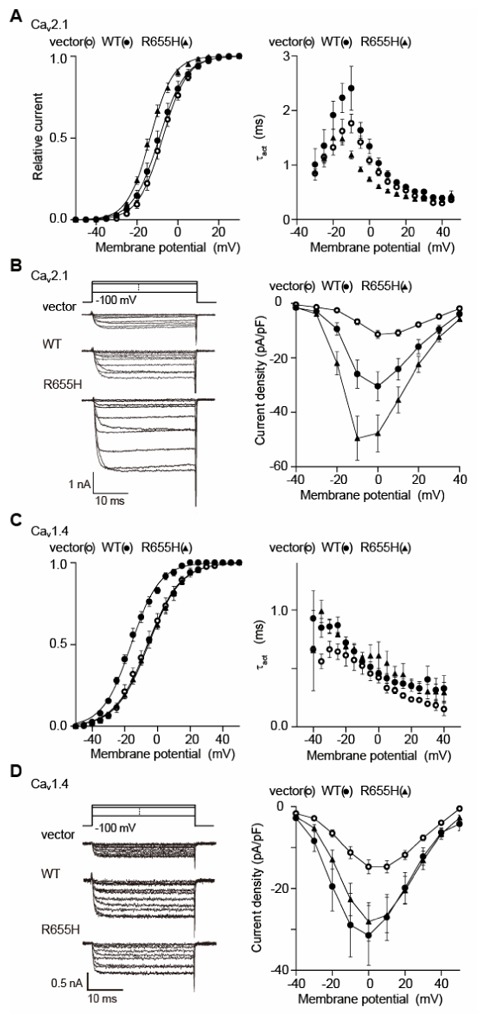
(A) Effects of WT and R655H on activation properties of Cav2.1 currents in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. Left panel: effects of WT and R655H on activation curves of Cav2.1 currents. Tail currents elicited by repolarization to −60 mV after 5-ms test pulse from −50 to 50 mV are used to determine activation curves. Right panel: effects on activation speed of Cav2.1 channels. Time constants are obtained by fitting the activation phase of currents elicited by 5-ms test pulse from −30 mV to 45 mV with a single exponential function. (B) Effects of WT and R655H on P/Q-type Cav2.1 current amplitude. Left panel: representative traces for Ba2+ currents evoked by test pluses from −40 mV to 50 mV with 10-mV increments in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. Right panel: current density-voltage (I–V) relationships of Cav2.1. The Vh is −100 mV. (C) Effects of WT and R655H on activation properties of Cav1.4 currents in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. Left panel: effects of WT and R655H on activation curves of Cav1.4 currents. Right panel: effects on activation speed of Cav1.4 channels. (D) Effects of WT and R655H on L-type Cav1.4 current amplitude. Left panel: representative traces for Ba2+ currents on application of test pluses from −40 mV to 50 mV with 10-mV increments in BHK cells co-expressing α2/δ and β4b. Right panel: I–V relationships of Cav1.4. The Vh is −100 mV.
