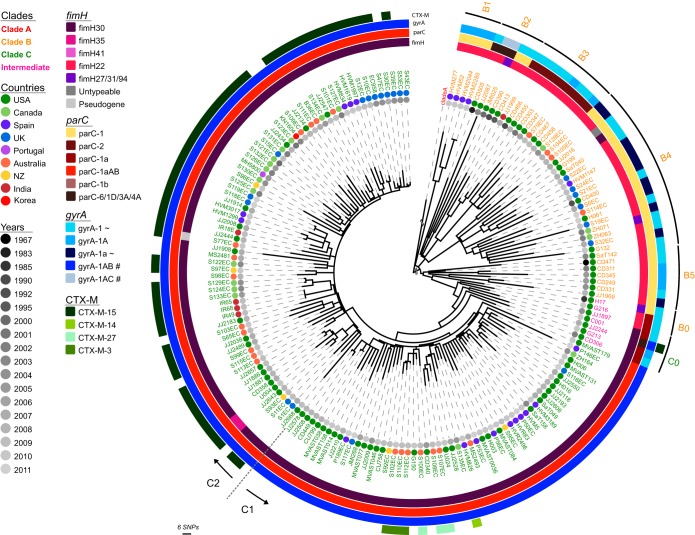
FIG 2 .
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of ST131 strains. The phylogram was built from 5,471 nonrecombinant SNPs using maximum likelihood (ML). Branch support was performed by 1,000 bootstrap replicates (see Fig. 2B in the supplemental material). The scale bar indicates the number of substitution SNPs. Taxon labels for clades A, B, and C are colored red, orange, and green, respectively. Seven strains sharing intermediate characteristics between clades B and C are colored pink. Of note, clade A strains were collapsed and the clade A-specific branches shortened for display. Metadata are represented as circles as follows: year of isolation in gray and gradient and geographical region in assorted colors as depicted in the legend. Allelic profiling information is shown as colored strips surrounding the phylogram (from inner to outer) for the fimH, parC, gyrA, and CTX-M genes. Two additional distinctions were made for some fimH variants: “Untypeable” corresponds to a strain with a truncated or missing fimH gene, and “Pseudogene” corresponds to a strain in which fimH is disrupted by an insertion sequence. Clades B0 to B5 and C0 subclades are shown as arcs in the outermost ring, with arrows and dotted lines denoting the division between subclades C1 and C2.