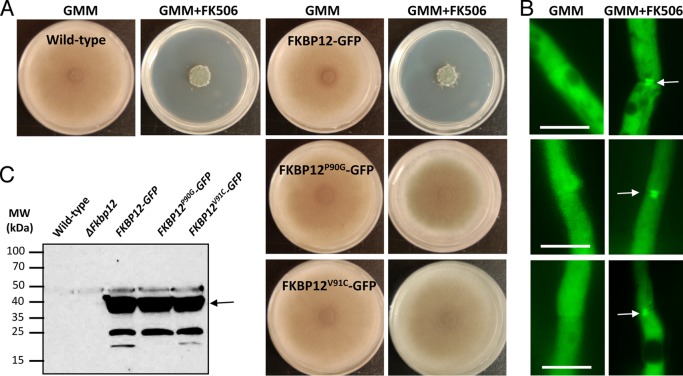
FIG 6 .
In vivo analysis of mutant A. fumigatus FKBP12s. (A) Radial growth of the WT strain (akuBKU80) and the strains expressing WT FKBP12-GFP and the mutated versions of FKBP12 [FKBP12(P90G) and FKBP12(V91C)] tagged with GFP were assessed after 5 days on GMM agar with or without supplementation with FK506 (100 ng/ml). Note the resistance of the FKBP12(P90G)- and FKBP12(V91C)-producing strains to FK506. (B) Strains expressing WT FKBP12-GFP and the mutated versions of FKBP12 [FKBP12(P90G) and FKBP12(V91C)] tagged with GFP were cultured in liquid GMM in the absence or presence of FK506 (100 ng/ml) on coverslips for 18 to 20 h and observed for the localization of FKBP12 by fluorescence microscopy. Note the complete cytosolic localization of FKBP12s in the absence of FK506. Arrows indicate the translocation of FKBP12s to the hyphal septa in the presence of FK506 indicative of their binding to CaN at the hyphal septa. Scale bar, 10 µm. (C) Western analysis performed with the anti-GFP polyclonal primary antibody and a peroxidase-labeled anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody. The arrow indicates the ~37-kDa FKBP12-GFP fusion protein. The values on the left are molecular masses in kilodaltons.