FIGURE 8.
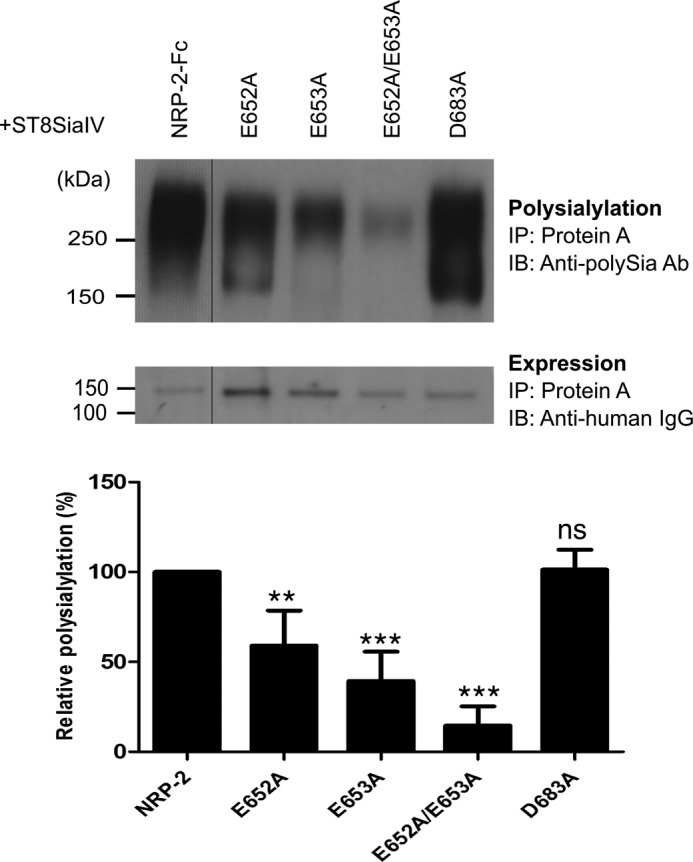
Glu652 and Glu653 on the surface of NRP-2 MAM domain are important for the polysialylation of NRP-2. Acidic residues Glu652 and Glu653 were mutated in NRP-2-Fc. As a control, Asp683 was also mutated to alanine in NRP-2-Fc. NRP-2-Fc and its mutants were expressed with ST8SiaIV in COS-1 cells, recovered from the cell medium using protein A-Sepharose beads (IP), and immunoblotted (IB) with the anti-polySia 12F8 antibody to evaluate the effect of the MAM domain mutations on NRP-2 polysialylation (top). Relative protein expression levels were determined by removing the bound protein from an aliquot of the protein A-Sepharose beads by boiling and immunoblotting with an HRP-linked anti-human IgG (bottom). The line separating NRP-2-Fc and the E652A mutant reflects the removal of an extraneous lane so that the mutants and NRP-2-Fc can be more directly compared. Quantification of the experimental results was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” with data from four different experiments with error bars representing S.D. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired Student's t tests. **, 0.001 < p < 0.01; ***, 0.0001 < p < 0.001; ns, p ≥ 0.05 with respect to wild type NRP-2, which is normalized to 100%.
