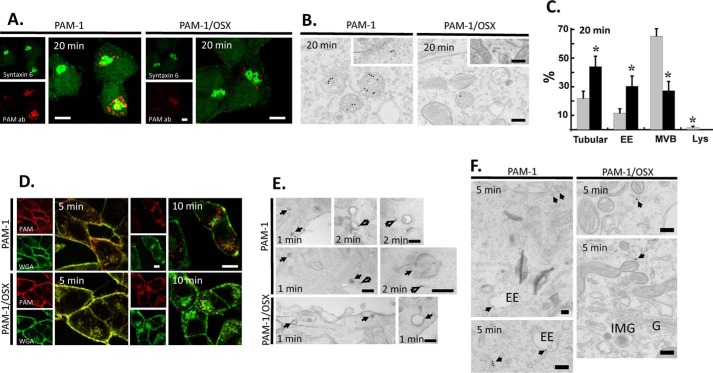
FIGURE 7.
Endocytic trafficking of PAM-1/OSX is altered. The endocytic trafficking of PAM-1 and PAM-1/OSX was monitored by incubating live cells with ectodomain antibody to PAM. A, cells incubated with PAM antibody for 5 min were chased for 15 min, fixed, and permeabilized; endogenous syntaxin 6 and internalized ectodomain antibody were visualized. Scale bars, 10 μm. B, cells incubated with PAM antibody-gold complexes at 4 °C were visualized after a 20-min chase at 37 °C. Representative images are shown as follows: three labeled multivesicular bodies are seen in the PAM-1 cell and one in the PAM-1/OSX cell; insets show labeled tubular structures. Scale bars, 200 nm. C, graph shows the percentage of total gold particles in tubular structures, early endosomes (EE), multivesicular bodies (MVB), and lysosomes (Lys) in PAM-1 (gray bars) and PAM-1/OSX (black bars) cells after the 20-min chase (mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.001). D, PAM-1 and PAM-1/OSX cells exposed to PAM antibody and to fluorescently tagged WGA for 5 min were rinsed and chased for 5 or 10 min before fixation; internalized antibody was visualized after permeabilization. Scale bars, 10 μm. E and F, PAM-1 and PAM-1/OSX cells kept on ice were incubated with PAM antibody-gold complexes and WGA-HRP; cells were fixed after a chase incubation at 37 °C for 1, 2, or 5 min. E, after a 1- or 2-min chase, co-localized PAM antibody-gold complexes and peroxidase product are indicated by arrows; open arrows mark PAM-1 separated from WGA and in tubules. Scale bars, 200 nm. F, after the 5-min chase, antibody/gold particles were found in tubular structures and early endosomes (EE) in PAM-1 cells; in PAM-1/OSX cells, antibody/gold particles were confined to tubular structures localized peripherally or near the Golgi complex (G, Golgi stack; IMG, immature secretory granule). Scale bars, 200 nm.