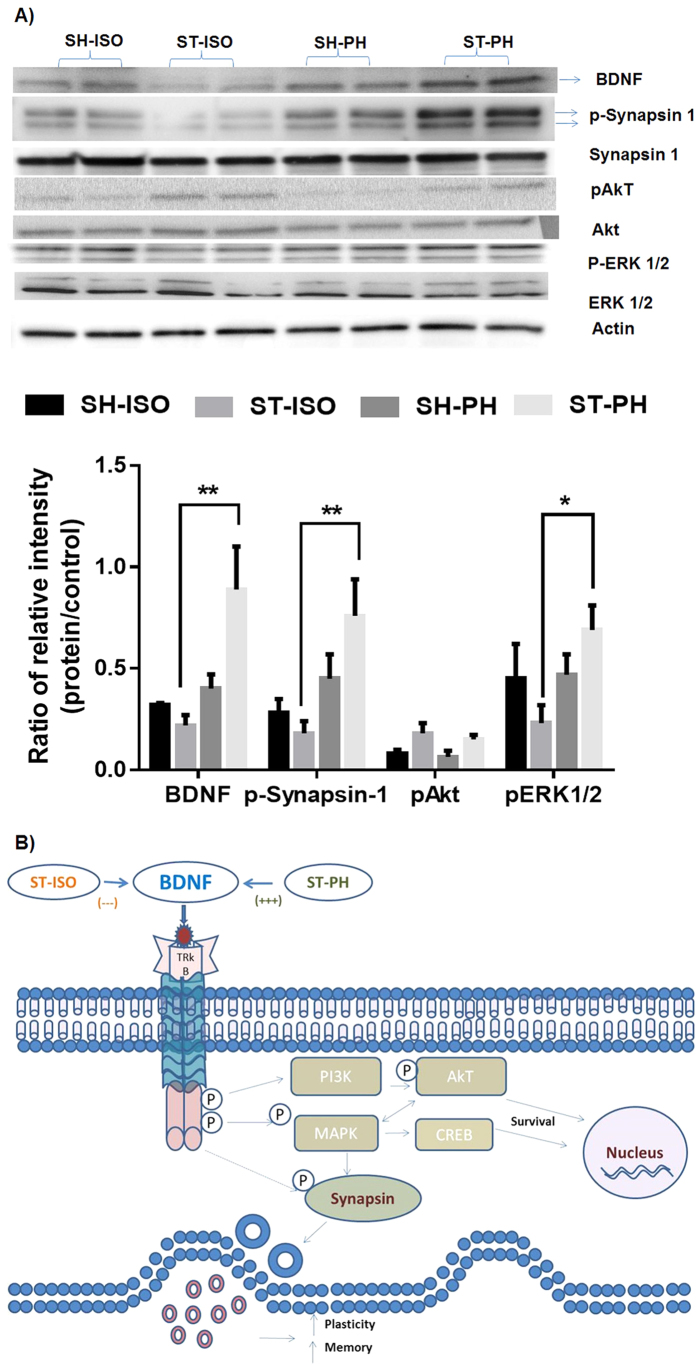
Figure 8.
(A) Activation of BDNF-MAPK-synapsin pathways in pair-housed mice after stroke. Brain tissue homogenates 4 weeks after pair housing showed an up-regulation of BDNF in ST-PH mice. Western blot analysis shows upregulation of p-synapsin and pERK1/2 in ST-PH mice as compared to ST-ISO mice. pAkt levels were elevated in both stroke groups. (B) Schematic illustration of the potential mechanism by which pair housing, BDNF, TrK-B receptor and the downstream signaling pathways could enhance neurobehavioral recovery. SI decreases BDNF levels in the brain. BDNF after binding to its receptor can activate MAPK via phosphorylation. Activation of MAPK leads to enhanced phosphorylation and activation of synapsin-1 which increases the synaptic release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA, increasing synaptic transmission, LTP, memory, cognition and recovery after stroke.