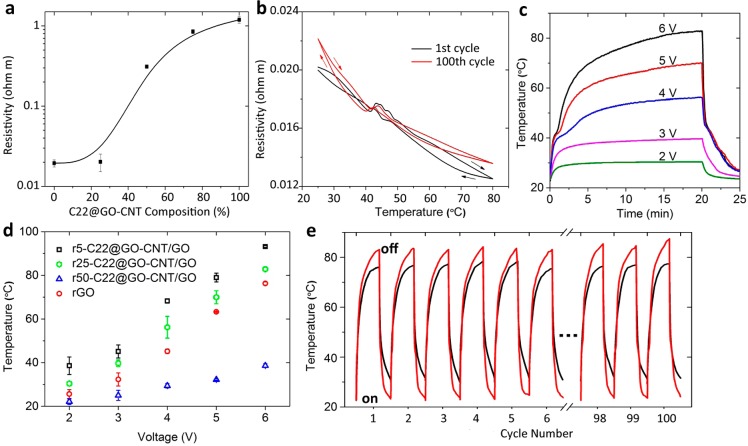
Figure 5.
Electrical conductivity and electrothermal performance of rC22@GO–CNT/GO composites. (a) The resistivity of rC22@GO–CNT/GO composite varies with the volume concentration of C22@GO–CNT. (b) As a function of temperature, the resistivity curves of the 1st and 100th thermal cycles change slightly, indicating the conductive structure is stable. (c) Temperature evolution curves of r25-C22@GO–CNT/GO under constant voltages of 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 V. (d) As a function of voltage, the balanced surface temperatures obtained at 20 min heating are demonstrated. The samples of r5-C22@GO–CNT/GO, r25-C22@GO–CNT/GO, 50-C22@GO–CNT/GO, and neat rGO heater were studied. (e) A collection of temperature evolution curves of r25-C22@GO–CNT/GO composite and neat rGO heater under 6 V repeated for 100 cycles.