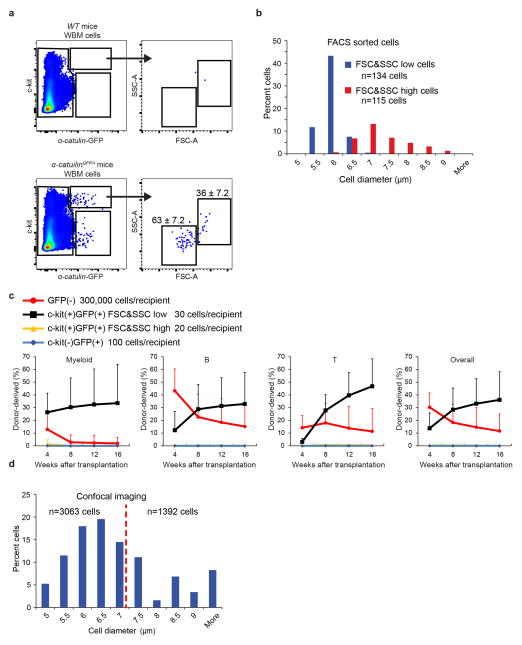
Extended data figure 5. All HSC activity resides among α-catulin-GFP+ckit+ cells with low forward and side scatter.
a, Most α-catulin-GFP+ckit+ cells (63±7.2%) had low forward and side scatter but a distinct minority population (36±7.2%) had higher forward and side scatters that were not typical of HSCs. b, We sorted the low scatter and the high scatter α-catulin-GFP+ckit+ cell populations gated in panel a and measured their diameters (3 independent experiments). c, Competitive reconstitution assays in irradiated mice revealed that all HSC activity resided in the low scatter cell fraction. For each recipient mouse, the indicated donor cells (based on the number of cells from each population contained within 300,000 bone marrow cells) were transplanted into irradiated mice along with 300,000 recipient bone marrow cells (mean±s.d. from 2 independent experiments with 20 total recipient mice in the GFP(−) group, 14 total recipient mice in the c-kit(+)GFP(+) FSC&SSC low group, 11 total recipient mice in the c-kit(+)GFP(+) FSC&SSC high group and 9 total recipient mice in the c-kit(−)GFP(+) group). d, The size distribution of all α-catulin-GFP+ckit+ cells identified by confocal microscopy in bone marrow plugs from the tibia diaphysis (6 bones analyzed in 6 independent experiments). In keeping with the flow cytometry data, the largest 40% of imaged cells were not considered HSCs, excluding all cells with diameter larger than 7 μm.