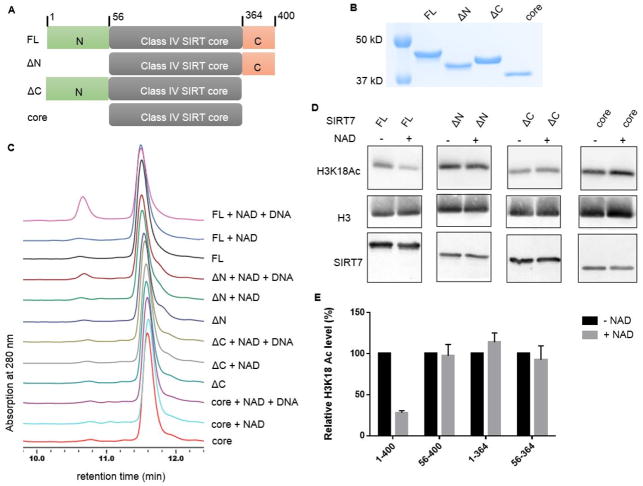
Figure 3. Both the N- and C- termini of SIRT7 are important for its activation by DNA.
(A) Scheme showing the full length (FL, residue 1-400), N-terminal deletion (ΔN, residue 56-400), C-terminal deletion (ΔC, residue 1-364), and core domain (56-364) of SIRT7. (B) Coomassie blue-stained gel showing the purity of SIRT7 deletion mutants. (C) HPLC traces showing the activity of different SIRT7 deletion mutants with and without dsDNA on H3K18 Ac peptide. (D) The deacetylase activities of SIRT7 FL and deletion mutants on H3K18 Ac on chromatin substrates. Reactions without NAD were used as negative controls. (E) Quantification of the Western blot results in (D). The H3K18 Ac level in each reaction was normalized by the amount of histone H3 protein. The relative H3K18 Ac level was calculated by setting the level of negative control to 100%.