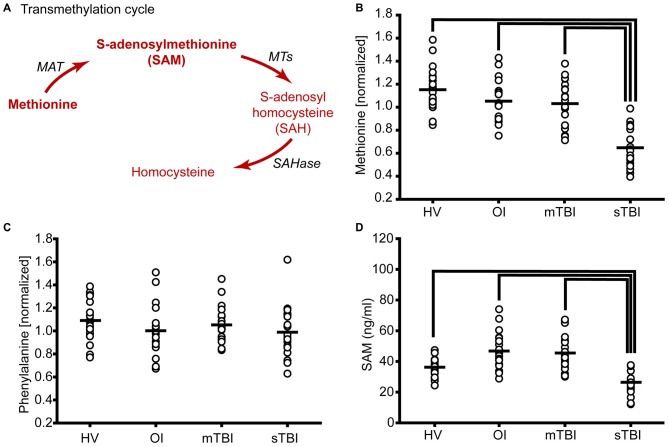
Figure 1.
Severe traumatic brain injury (sTBI) reduces plasma methionine and metabolism through the transmethylation pathway. (A) Schematic showing the metabolism of methionine via the transmethylation pathway. Molecules detected and measured are presented in bold text. Key enzymes are indicated by italic text. The plasma levels of (B) methionine were significantly reduced as a result of TBI. (C) S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) was significantly reduced in sTBI compared to healthy volunteers (HV) and patients with a mild TBI (mTBI). When the data were segregated by gender, similar changes in both (D) methionine and (E) SAM were observed in males and females. MAT: methionine adenosyltransferase; MTs: methyltransferases; SAHase: S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. Horizontal bar indicates mean. *p < 0.05.