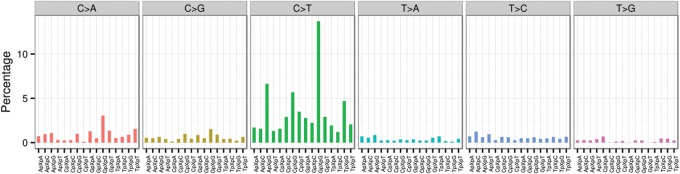
Figure 4.
The mutational signature of the granular cell tumor. Each single-nucleotide substitution is categorized into the 96 distinct trinucleotide mutation types, depending on the substitution class (C>A, C>G, C>T, T>A, T>C, or T>G) and the neighboring bases (A, C, G, or T) immediately 3′ and 5′ to the mutated base. The number of mutations in each category is divided by the abundance of its trinucleotide in the reference genome to give a fractional count. The fractional count is then normalized and displayed as the percent attribution to a specific mutation type in the plot.