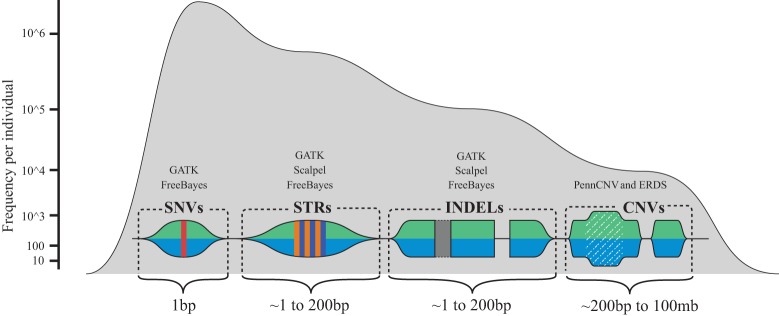
Figure 2.
A conceptual map of human sequence variation. Here, we show approximate sizes, as well as the associated signature, of the various different types of human sequence variation that can be currently detected with whole-genome sequencing (WGS), microarray data, and informatics technologies used in this work. The frequency axis shows the approximate frequency of the various genetic variation types that are currently detectable via germline WGS combined with microarray data. Above the visual signatures of the different types of human sequence variation, the general names of the different informatics software tools for detecting the variation are noted which include, the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK), Scalpel, PennCNV, the estimation by read depth with single-nucleotide variants (ERDS) CNV caller, and the FreeBayes caller.