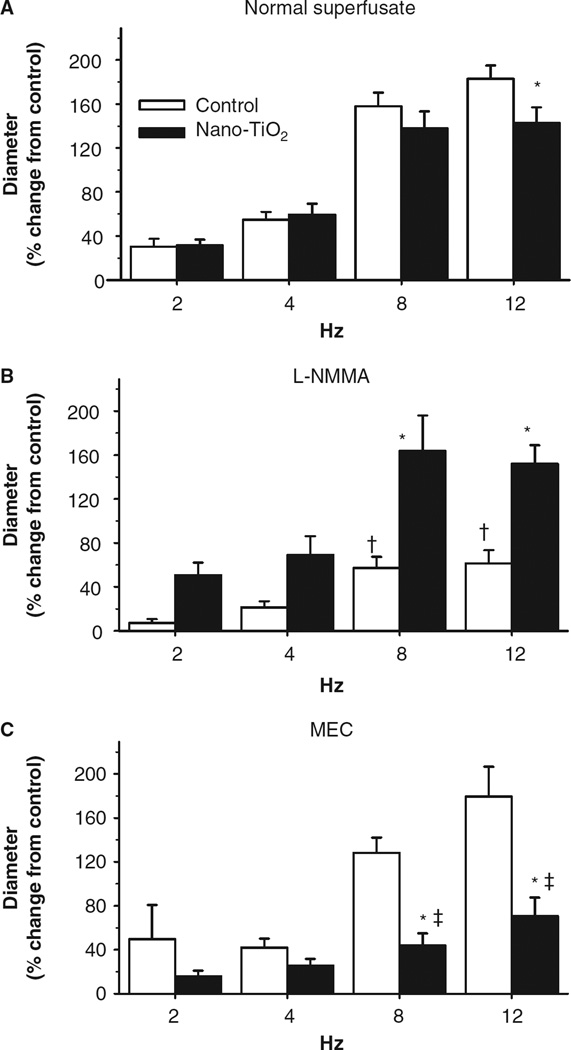
Figure 5.
Nanoparticle inhalation attenuates functional arteriolar dilation during active hyperaemia. (A) Nano-TiO2 exposure reduces arteriolar vasodilation to metabolic stimuli (n = 23 control, 31 nano-TiO2-exposed arterioles). (B) Inhibition of NO production with NG-monomethyl-l-arginine (L-NMMA) attenuates arteriolar dilation in control animals but not nano-TiO2 exposed (n = eight control, nine nano-TiO2-exposed arterioles). (C) Conversely, inhibition of cyclooxygenase impairs arteriolar dilation in nano-TiO2-exposed animals compared with control (n = 9 control, 15 nano-TiO2-exposed arterioles). MEC, meclofenamate. Values are means ± SE. *p < 0.05 vs. control, †p < 0.05 vs. control normal superfusate at the same frequency, ‡p < 0.05 vs. nano-TiO2-exposed normal superfusate at the same frequency.