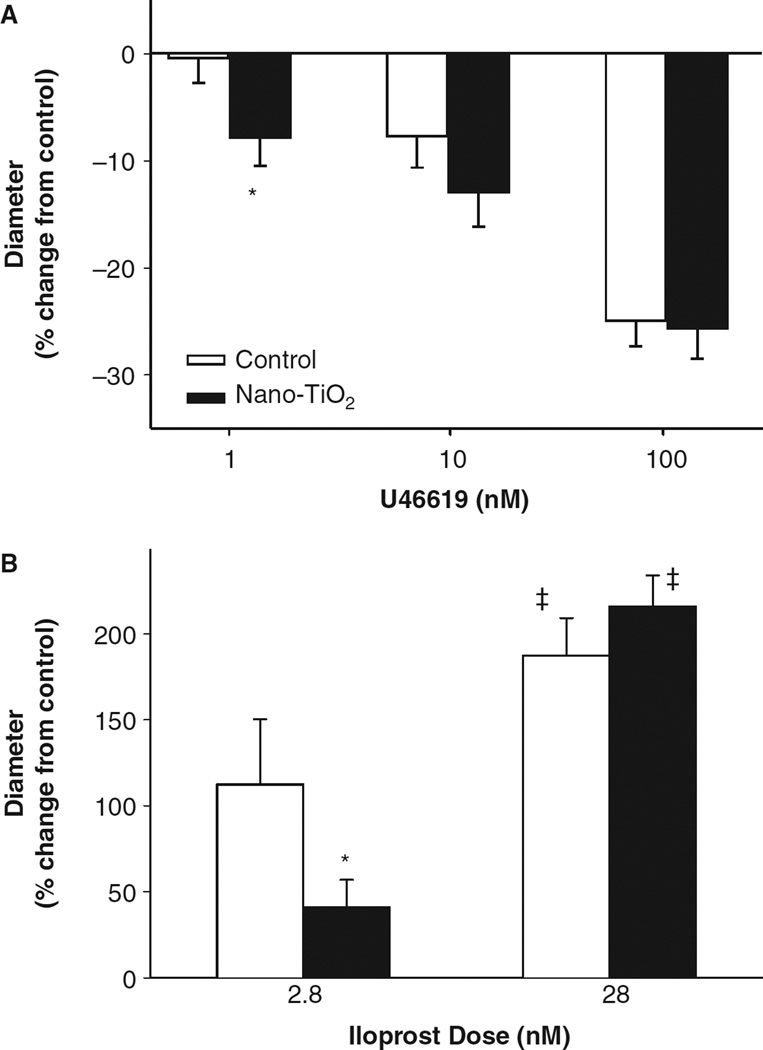
Figure 6.
Pulmonary nanoparticle exposure alters arteriolar responsiveness to thromboxane A2 (TxA2) and prostacyclin mimetics. (A) Superfusion of the spinotrapezius muscle with U46619, a TxA2 mimetic, significantly enhanced arteriolar constriction following nano-TiO2 exposure compared with control animals at 1 nM (n = 16 control, 13 nano-TiO2-exposed arterioles). (B) Iloprost superfusion led to a dose-dependent arteriolar dilation that was significantly blunted at 2.8 nM following nano-TiO2 exposure (2.8 nM n = 9 control and n = 13 nano-TiO2 exposed; 28 nM n = 11 control and n = 16 nano-TiO2-exposed arterioles). Values are means ± SE. *p < 0.05 vs. control exposure, ‡p < 0.05 vs. 2.8 nM iloprost.