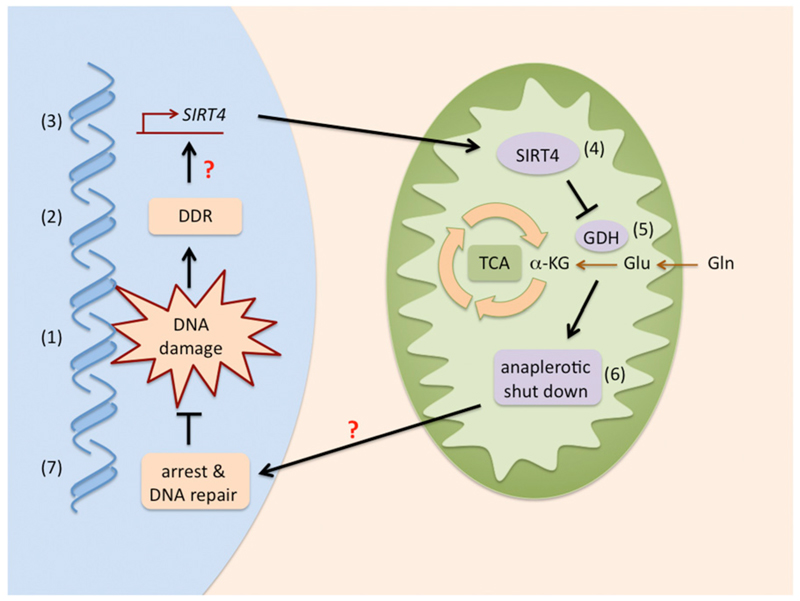
Figure 1. SIRT4: The Glutamine Gatekeeper.
DNA damage (1) elicits the DDR (2) that, through undefined mechanisms (indicated with a question mark), results in enhanced SIRT4 transcription (3) and higher SIRT4 activity in the mitochondria (4). In turn, SIRT4 inhibits glutamine conversion into αKG by inhibiting glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) (5). Decreased αKG shuts down the anaplerotic replenishment of the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) (6), which, through mechanisms that remain to be clarified (question mark), result in arrest and DNA repair (7).