Extended Data Figure 5. Ece1-III62–93 is a cytolytic α-helical peptide.
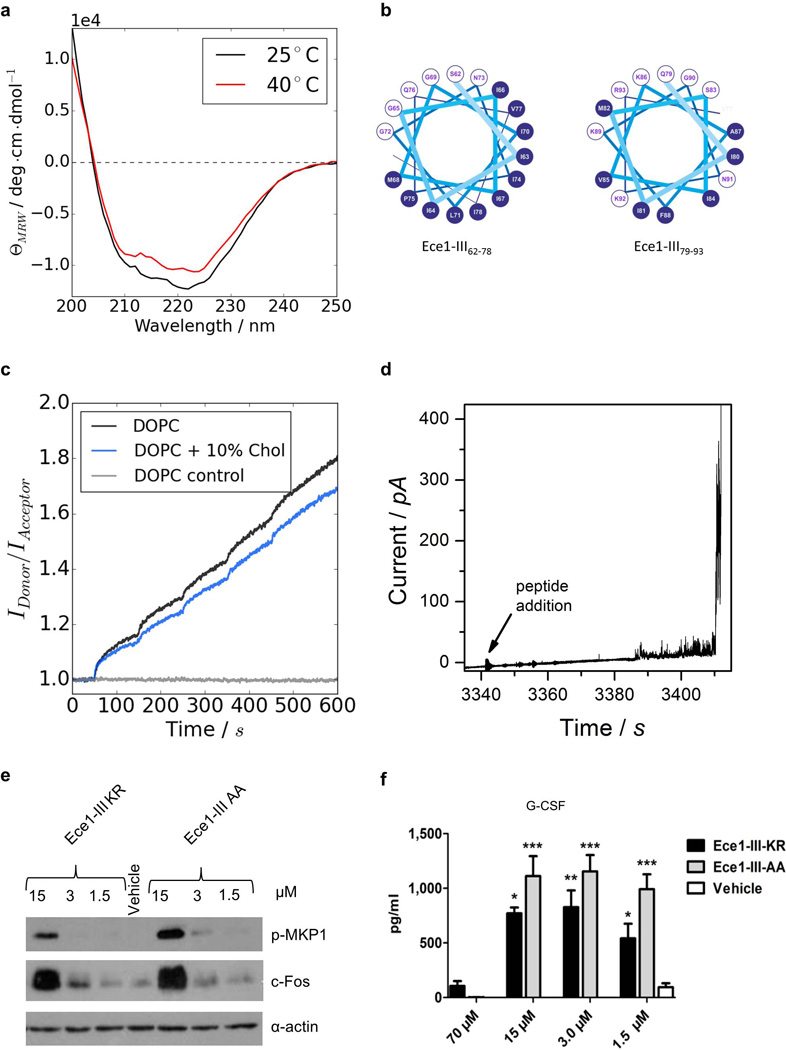
(a) Circular dichroism spectra showing the α-helical conformation of Ece1-III62–93 in buffer (100 mM KCl, 5 mM HEPES, pH 7). Increasing the temperature from 25°C to 40°C did not affect the stability of the α-helical structure. (b) Diagram to illustrate the amphipathic nature of Ece1-III62–93 (residues 62–78, left panel; residues 79–93, right panel). Residues with hydrophobic or polar/charged side chains are displayed with a blue and white background, respectively. Modified from output generated in PEPWHEEL (http://emboss.bioinformatics.nl/cgi-bin/emboss/pepwheel). (c) Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) experiments show the intercalation of Ece1-III62–93 into lipid liposomes (10 µM) composed of DOPC in the absence or presence of cholesterol. Peptide titration of Ece1-III62–93 to liposomes showed slightly enhanced intercalation for pure DOPC. (d) Ece1-III62–93 induced the permeabilization of planar lipid membranes composed of DOPC. The graph shows heterogeneous and transient lesions leading finally to a rupture of the membrane. Ece1-III62–93 concentration was 0.125 µM. (e) Induction of p-MKP-1 and c-Fos 2 h in TR146 cells post stimulation (p.s.) with Ece1-III62–93KR or Ece1-III62–93AA(f) Secretion of G-CSF from TR146 cells 24 h p.s. with Ece1-III62–93KR or Ece1-III62–93AA. Data shown are representative (a-e) or mean (f) of at least three biological replicates. Error bars show ± SEM. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA (f). * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001 (compared with vehicle control). For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1.
