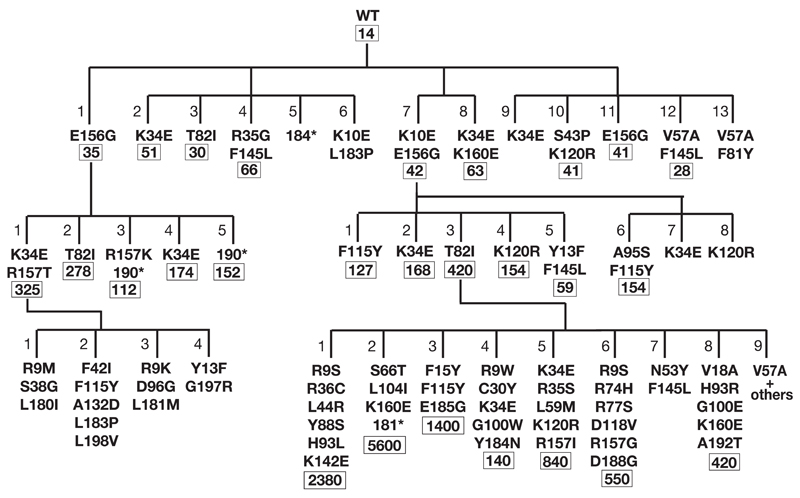
Figure 2.
Dynasty of AID upmutants selected by papillation screen. Upmutants obtained in three successive rounds of mutagenesis with mutants obtained from individual PCR-mutagenesis experiments grouped as families of siblings. The additional amino acid substitutions introduced in each round of mutagenesis are indicated with the numbers below giving the mean frequency of mutation to Rifr relative to vector. * indicates a C-terminal truncation caused by introduction of a premature stop codon at the indicated codon. Individual mutants are numbered according to their dynastic origin: thus, for example, Mut7 (K10E/E156G) is the parent of Mut7.1 (K10E/E156G/F115Y).