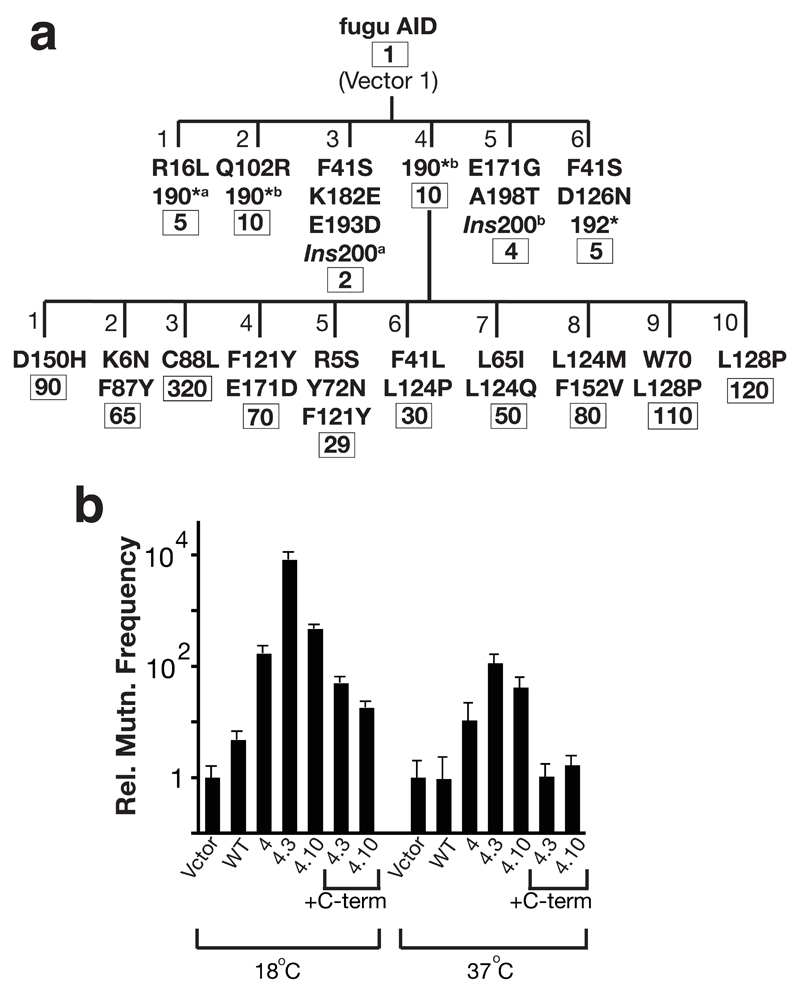
Figure 4.
Upmutants of fugu AID. (a) Dynasty of upmutants of fugu AID selected at 37 °C. * indicates a C-terminal truncation caused by introduction of a premature stop codon; *a and *b indicate different single nucleotide substitutions at codon 190 causing the premature stop codon; Ins200a and Ins200b indicate different single nucleotide insertion mutations at codon 200 which cause the C-terminal region to be read out-of-frame. Numbers below gives the mean frequency of mutation to Rifr relative to vector. (b) The frequency of mutation to Rifr relative to vector-only transformants at either 18 °C or 37 °C is shown for E. coli K16 transformed with plasmids encoding wild type or mutated fugu AID as indicated. Derivatives of Mut4.3 and 4.10 were constructed in which the nonsense mutation at 190 had been reverted, thereby yielding a wild-type C-terminus (+C-term).