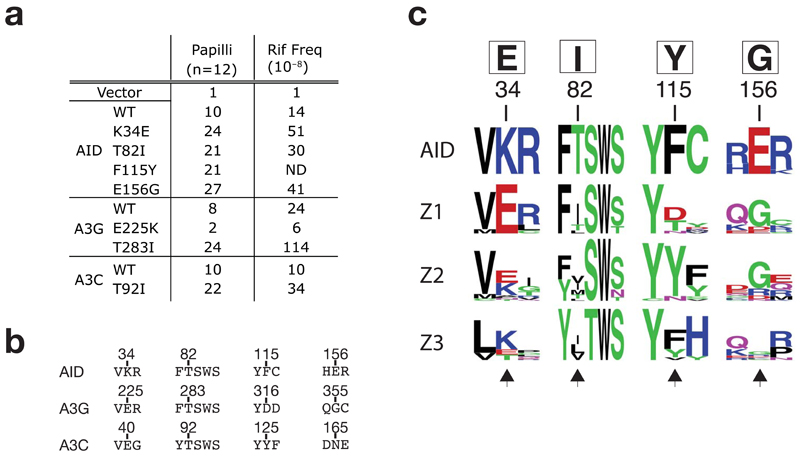
Figure 7.
Comparison of AID with APOBEC3s. (a) Mutator activity of mutants of AID, APOBEC3G and APOBEC3C carrying the indicated single amino acid substitutions as monitored in the papillation and rifampicin-resistance assays. (b) Sequence alignments of selected regions of AID, APOBEC3G and 3C. Number above the sequences indicate the positions of the residues in the parental sequence. (c) Web LOGO alignment (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/) depicting amino acid conservation surrounding the major sites of upmutation of AID and the homologous regions in the Z1, Z2 and Z3 domains of mammalian APOBEC3s (cow, sheep, pig, dog, peccary, horse, cat, dog, mouse, rat, human and macaque: sequence accession numbers are provided in supplementary Table 1). Any sequence with over 90% amino acid identity to any other sequence was discarded from generation of the LOGO profiles. The AID upmutations identified in this work are shown in the box above the numbered residues. Black arrows at the bottom of the alignment highlight the homologous residues in the APOBEC3s.