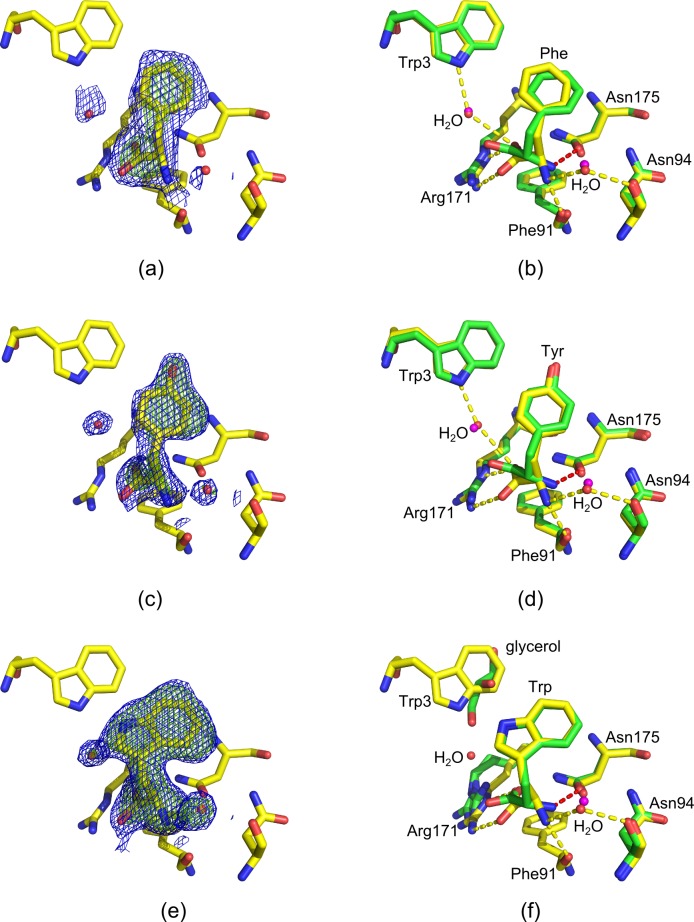
Fig 4. Binding modes of aromatic d-amino acids in the Phe site.
Comparison of binding modes of d-Phe, d-Tyr and d-Trp (pdb id 5E2L, 5E4N and 5E5G respectively, shown as yellow sticks, waters shown as red spheres) with l-Phe, l-Tyr and l-Trp (pdb id 2YPO, 2YPP and 5EX4 respectively, shown as green sticks, waters shown as magenta spheres). The l-amino acids establish an additional hydrogen bond between the amino moiety of the ligand and the side chain carbonyl group of Asn175 on the protein (highlighted as red dashes) when compared to the d-amino acids (other interactions shown as yellow dashes). 2Fo-Fc omit maps contoured at 1.0 σ (blue mesh) and Fo-Fc omit maps contoured at 3.0 σ (green mesh). (a) Omit map showing the density into which d-Phe and two water molecules were modelled. (b) Comparison of l-Phe and d-Phe binding mode in the Phe site. (c) Omit map showing the density into which d-Tyr and two water molecules were modelled. (d) Comparison of l-Tyr and d-Tyr binding mode in the Phe site. (e) Omit map showing the density into which d-Trp and two water molecules were modelled. (f) Comparison of l-Trp and d-Trp binding mode in the Phe site.