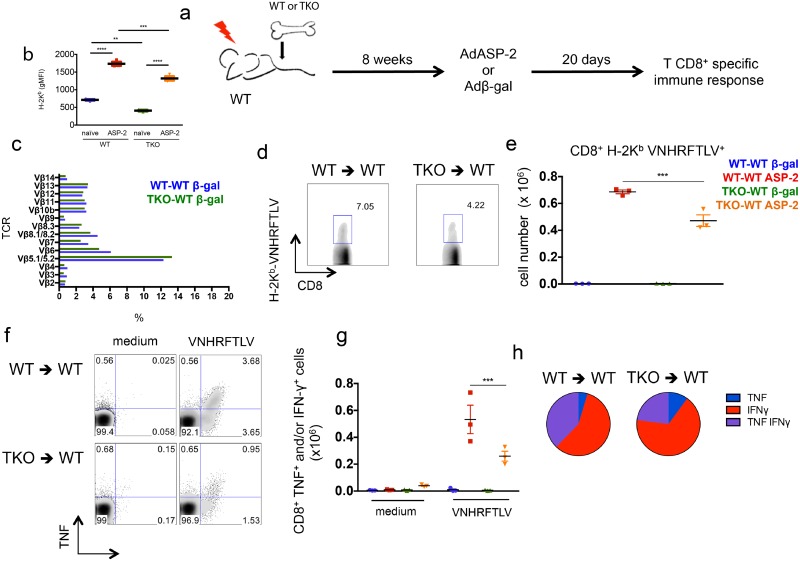
Fig 9. Impaired immunity of specific CD8+ T cells upon genetic vaccination of WT mice reconstituted with immunoproteasome-deficient bone marrow.
(a) Experiment design: WT mice were irradiated and reconstituted with WT (WT-WT) or TKO (TKO-WT) bone marrow. After 8 weeks, chimeric mice were vaccinated with adenovirus 5 expressing beta-galactosidase (Adβ-gal) or ASP-2 (AdASP-2). Twenty days later, the response of CD8+ T cells was assessed in the spleen. (b) gMFI (geometric mean of fluorescence intensity) of H-2Kb staining of CD11c+ splenic cells from WT-WT and TKO-WT chimeras. (c) Staining of TCR Vβ chains gated in CD8+ T cells from WT-WT and TKO-WT chimeras genetically immunized with Adβ-gal. (d) Representative samples and (e) total numbers of specific CD8+ T cells stained with H-2Kb-VNHRFTLV pentamers. (f) Representative samples and (g) total numbers of CD8+ splenic cells positively stained with anti-TNF and/or anti-IFN-γ after ex vivo restimulation with the peptide VNHRFTLV corresponding to the immunodominant MHC class I-restricted epitope from ASP-2. (h) Combination of cytokines stained in responder CD8+ T cells from spleens of AdASP-2-vaccinated mice restimulated ex vivo with VNHRFTLV peptide. Results are shown as individual values and as the mean ± SEM for each group (n = 3). One representative of two independent experiments is shown. Asterisks indicate that the values observed for TKO mice were significantly lower than those for WT mice (**P<0.01 ***P<0.001 ****P<0.0001).