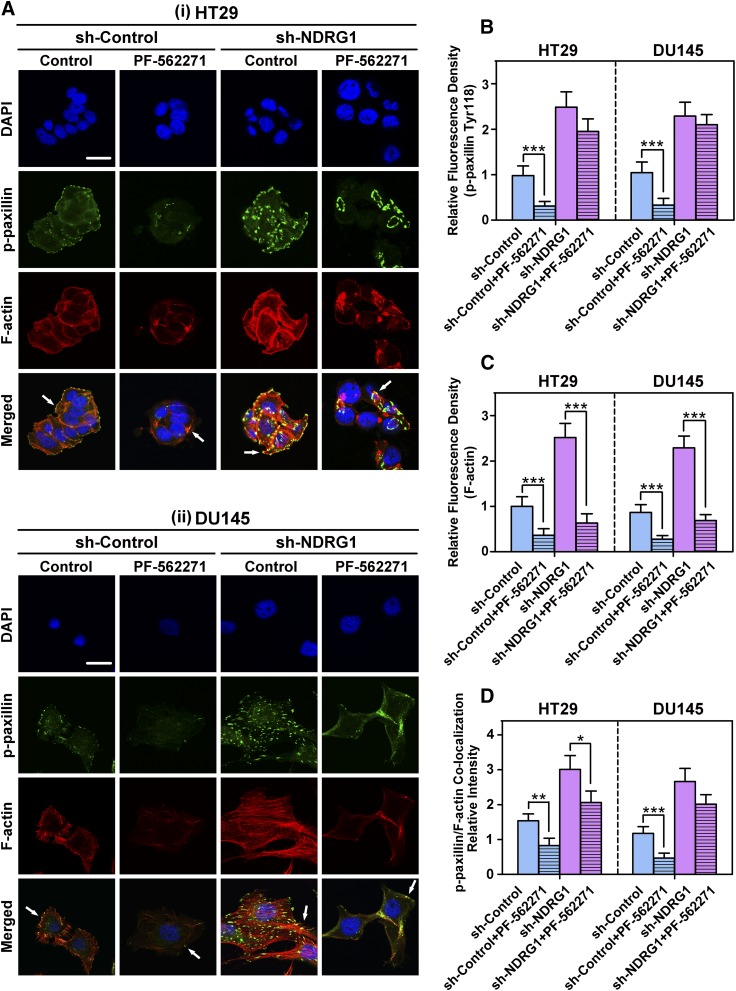
Fig. 7.
(A) The FAK phosphorylation inhibitor PF-562271 inhibits the formation of focal adhesions in both HT29 (i) and DU145 (ii) cells. Representative immunofluorescence images demonstrate the effect of PF-562271 on p-paxillin (Tyr118; green) and F-actin (red; stained with rhodamine-phalloidin) levels and their colocalization (yellow) in HT29 and DU145 cells (i.e., sh-Control and sh-NDRG1 cells). Cell nuclei (blue) were stained with DAPI. The yellow color after the electronic merge indicates colocalization of paxillin and stress fibers (see white arrows), indicating the formation of focal adhesions. Scale bar: 20 μm. Histograms show the relative fluorescence density for both p-paxillin (B) and F-actin (C) as well as the colocalization intensity of p-paxillin and F-actin (D). The histogram values in (B–D) are shown as mean ± S.D. (3–5 images from different fields). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 relative to the respective control cells.