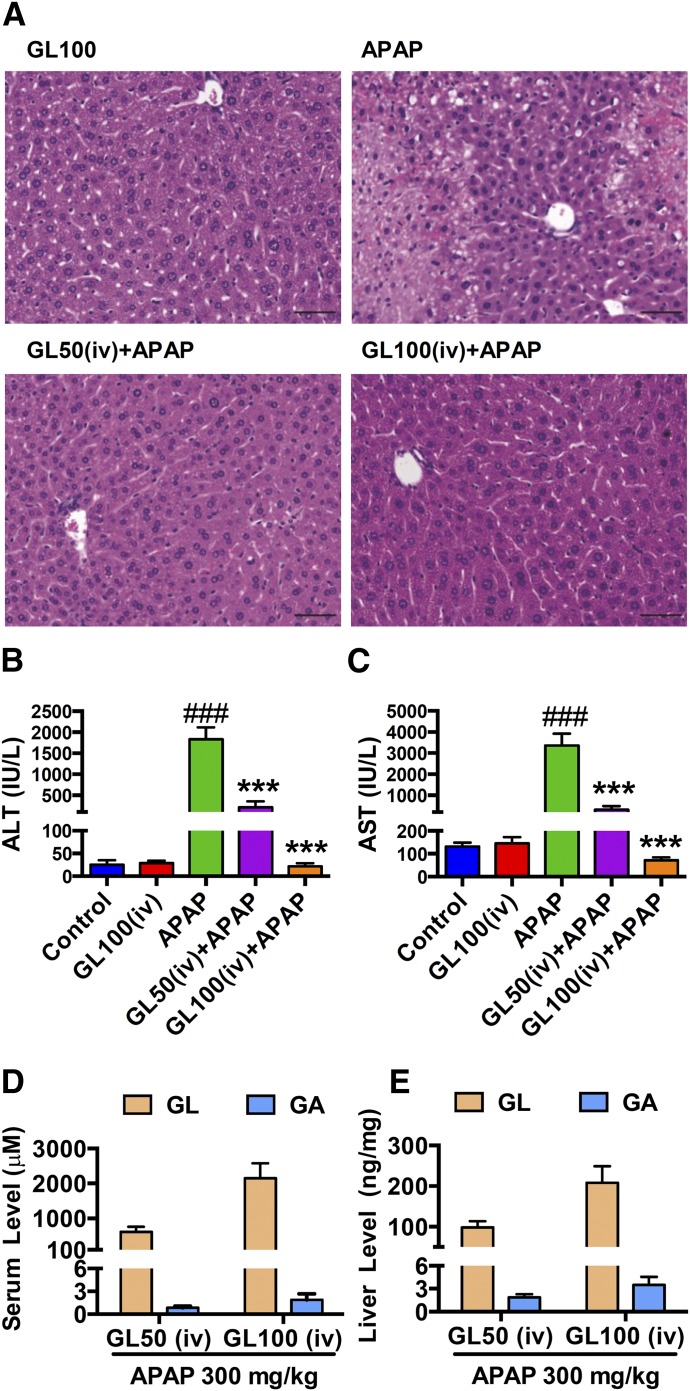
Fig. 3.
Intravenous injection of GL inhibits APAP-induced hepatotoxicity. (A) H&E-stained liver sections 4 hours after APAP challenge. Original magnification, 20×; black scale bar, 50 µm. (B, C) Serum ALT and AST levels. (D, E) GL and GA levels in serum and liver. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M., n = 5–8 in each group for all analyses. Control, saline-treated control mice; APAP, saline/APAP-treated mice; GL50 (iv) + APAP, GL 50 mg/kg (i.v.)/APAP-treated mice; GL100 (iv) + APAP, GL 100 mg/kg (i.v.)/APAP-treated mice; GL100 (iv), only GL 100 mg/kg (i.v.)-treated mice. ###P < 0.001 versus control mice; ***P < 0.001 versus APAP-overdosed mice.