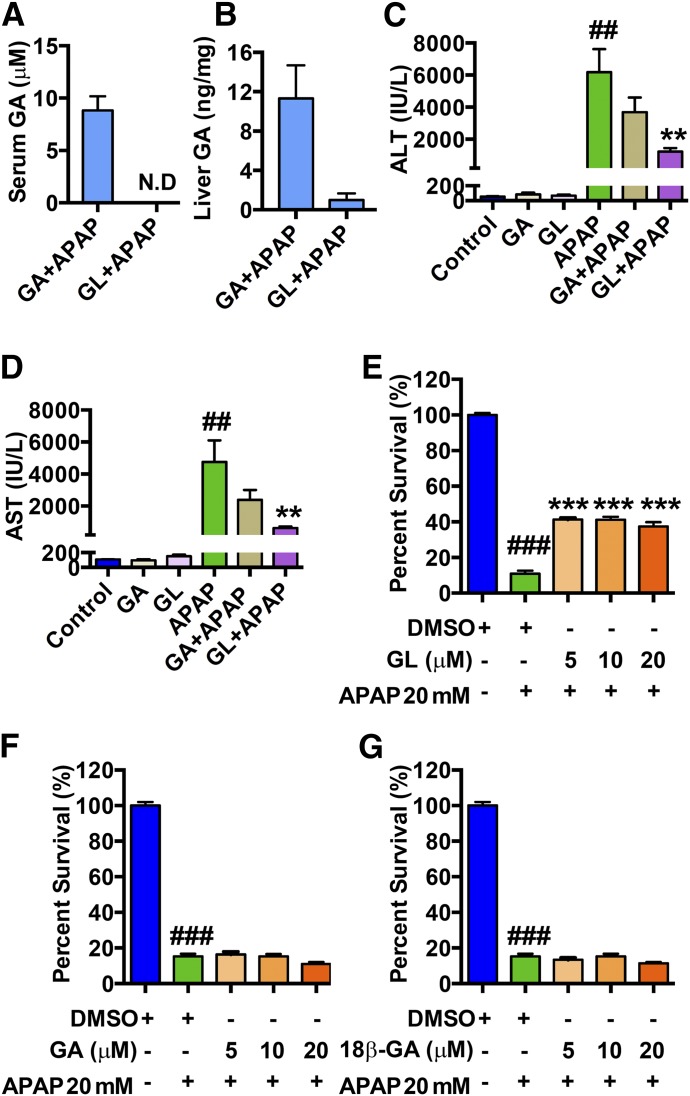
Fig. 5.
GL, rather than GA, prevents APAP-induced hepatocyte damage both in APAP-overdosed mice and APAP-treated LO2 cells. (A, B) GA exposure in serum (A) and in liver (B) in GA/APAP-treated mice and GL/APAP-treated mice. (C, D) Serum ALT and AST levels. (E) Cell viability of GL/APAP 20 mM-treated LO2 cells. (F) Cell viability of GA/APAP 20 mM-treated LO2 cells. (G) Cell viability of 18β-GA/APAP 20 mM-treated LO2 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M., n = 5–6 for both animal experiments and LO2 cell experiments. Control, saline-treated mice; GA, only GA 50 mg/kg-treated mice; GL, only GL 50 mg/kg-treated mice; APAP, saline/APAP-treated mice; GA + APAP, GA 50 mg/kg/APAP-treated mice; GL + APAP, GL 50 mg/kg/APAP-treated mice; ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 versus control mice or 0.1% DMSO-treated control LO2 cells. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus APAP-overdosed mice or 0.1% DMSO/APAP-treated LO2 cells.