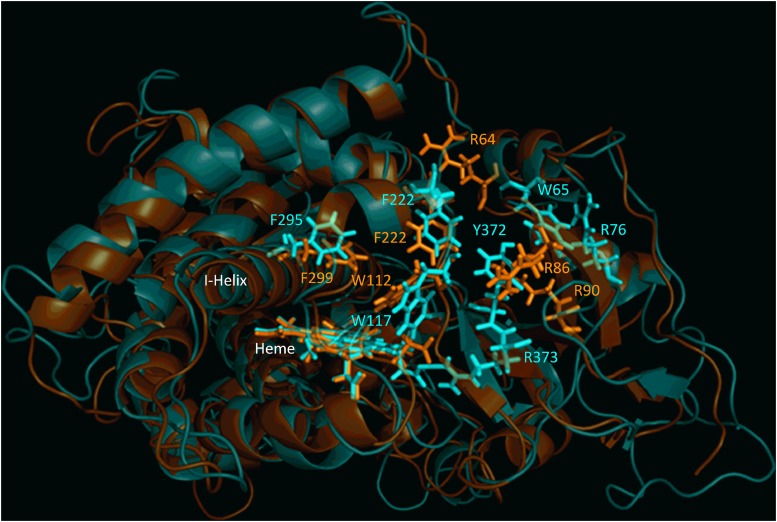
Fig. 2.
Structural alignment of CYP26A1 (orange) and CYP26B1 (cyan) homology models. Sequence alignment of the two homology models indicated a structural identity of 44.26% and an root-mean-square deviation value of 1.651. Structural similarity was observed for the portion of the active site of each enzyme that may contribute to hydrophobic binding interactions with a given ligand (Trp112, Phe222, and Phe299 for CYP26A1; Trp117, Phe222, and Phe295 for CYP26B1). The active-site volumes of CYP26A1 and CYP26B1 were estimated to be 918 Å3 and 977 Å3, respectively.