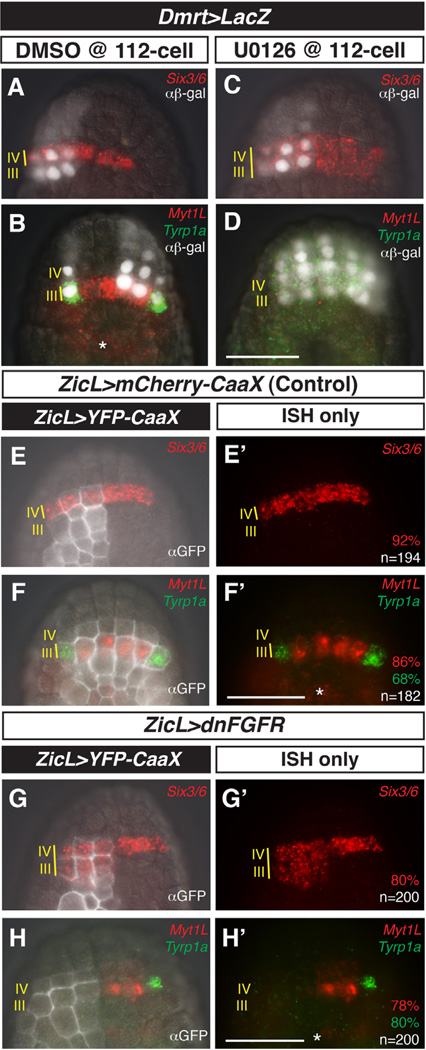
Fig. 2.
MEK/FGF-dependent patterning of rows III and IV of the anterior neural plate. (A–D) Embryos were electroporated with Dmrt > LacZ and treated with DMSO (control) or MEK inhibitor U0126 at the 110-cell stage, then fixed at mid-gastrula stage and processed for in situ hybridization with probes against Six3/6, MyT1L, and Tyrp1a and immunostaining with anti-β-galactosidase antibody (αβ-gal). In control embryos, Six3/6 expression is restricted to row IV (A). Myt1L is expressed in medial row III and Tyrp1a is expressed in the lateral a9.49 cells of row III (B). After treatment with U0126, Six3/6 expression expands posteriorly into row III (C) at the expense of Myt1L and Tyrp1a (D). (E–H′) Embryos electroporated with ZicL > YFP-CaaX alone or co-electroporated with ZicL > dnFGFR, fixed at mid-gastrula stage, and processed as in (A–D) except using anti-GFP antibody (αGFP). In control embryos, wild-type patterns of Six3/6, Myt1L, and Tyrp1a expression are observed (E–F′). ZicL > dnFGFR results in posterior expansion of Six3/6 and loss of Myt1L and Tyrp1a, recapitulating U0126 treatment (G–H′). (E–H) ISH overlayed with immunostaining and DIC channels. (E′–H′) ISH channels alone. Embryos in (A, C, E, G, H) are left–right mosaics, owing to unequal inheritance of electroporated plasmids; embryo in (B) also exhibits mosaic inheritance of the Dmrt reporter. Scale bars = 50 µm. Asterisks indicate expression of Myt1L in row I. See full quantitation of observed phenotypes in Supplementary Fig. 5.