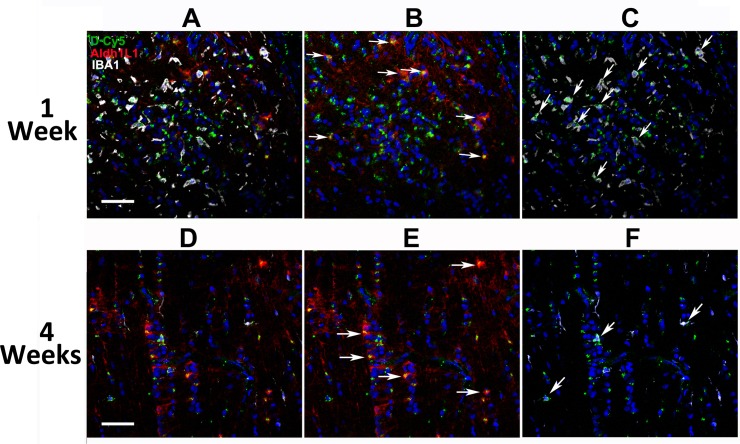
Fig 4. D-Cy5 persists in astrocytes and macrophages in the lamina after rNAION.
Higher magnification (20X) confocal analysis of the same regions seen in Fig 3 at 1 (A-C) and 4 (D-F) weeks. A. Three-channel (astrocyte, inflammatory cell, DAPI nuclear stain) confocal photo of D-Cy5 localization in the rat lamina 1week post-induction. Strong D-Cy5 signal is scattered within the lamina. B. Dual-channel photo showing D-Cy5 localization at high levels in astrocyte cytoplasm (arrows) in the lesioned area, revealed by Aldh1L1 immunostaining. C. Dual-channel photo showing D-Cy5 localization in inflammatory cells (arrows). D. Three-channel confocal photo of D-Cy5 localization in the rat lamina 4 weeks post-induction. D-Cy5 is reduced overall in the lesion area. E. Identification of astrocyte-specific D-Cy5 co-localization. D-Cy5 is still concentrated in astrocytes (arrows) but at considerably lower signal levels than at one week. F. Dual-channel (inflammatory cell-specific) D-Cy5 co-localization. D-Cy5 is still present in IBA1(+) cells (arrows) but at lower signal levels than at 1 week. Scale bars: 100μm.