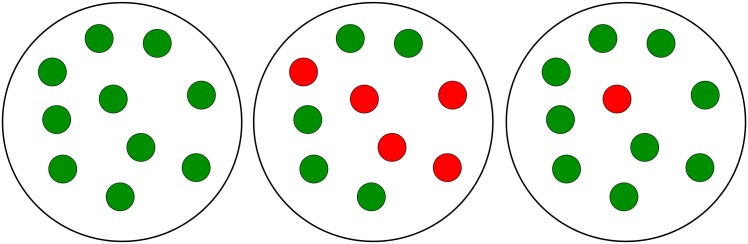
Fig 2. Homogeneous and heterogeneous (mixed) populations.
An example of a population consisting of 10 cells is shown. The left panel demonstrates a homogeneous G-population. The center panel demonstrates a heterogeneous (1:1)-population, where the homogeneous G- and R-subpopulations have equal number of cells. The right panel demonstrates a heterogeneous (9:1)-population formed of two unequal subpopulations which represent a spontaneous synchronization error, when one or a few toggles spontaneously flip from green (G) to red (R) states.