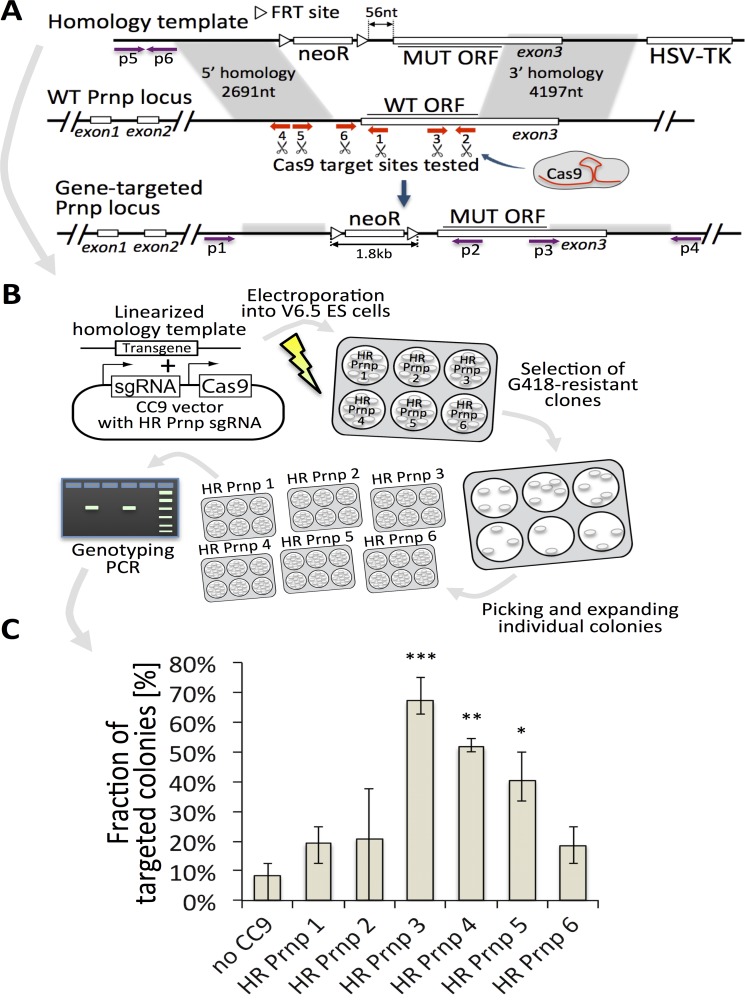
Fig 2. Evaluation of CRISPR/Cas9 for Prnp locus targeting.
(A) Schematic gene knock-in into the mouse Prnp locus using homology vector used for all targeting experiments. sgRNA binding sited were marked with white arrows. Primer binding regions used for subsequent genotyping of recombined clones were marked with purple arrows and designated p1 through p6. NeoR–neomycin resistance gene; FRT–Flp recombinase recognition site for removal of selection cassette after successful gene targeting. Regions of homology were shaded in grey. (B) Schematic of the experimental workflow for sgRNA evaluation. In brief, cells were electroporated with a Prnp targeting vector only, or Prnp targeting vector and a CC9 encoding guides #1-#6. In each case, targeting efficiency was assessed by long PCRs spanning the homology arms. (C) Histogram of CC9-assisted targeting efficiency for each of the six tested sgRNA compared to “no CC9” control (first column). “*”—p<0.05; “**”—p < 0.01; “***”—p < 0.001; Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test.